Fabrication of a magnetite/diazonium functionalized-reduced graphene oxide hybrid as an easily regenerated adsorbent for efficient removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution
- PMID: 35539153
- PMCID: PMC9078394
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00503f
Fabrication of a magnetite/diazonium functionalized-reduced graphene oxide hybrid as an easily regenerated adsorbent for efficient removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution
Abstract
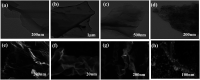
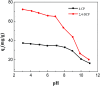
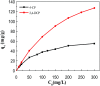
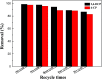
A magnetic hybrid nanomaterial, which contains magnetite (Fe3O4) particles and diazonium functionalized-reduced graphene oxide (DF-RGO), was fabricated via a three-pot reaction. First, the reduced graphene oxide (RGO) was synthesized via a redox reaction. Second, diazonium functionalized-RGO was prepared via a feasible chemical reaction. Third, Fe3O4 particles were loaded onto the surface of DF-RGO by covalent bonding, fabricating the M-DF-RGO hybrid. The fabricated hybrid was characterized by SEM, TEM, AFM, XRD, XPS, FT-IR, TGA, Raman spectroscopy, and magnetometry. The resulting M-DF-RGO hybrid possessed unique magnetic properties and was applied to remove 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) and 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) from aqueous solution. The adsorption of 4-CP and 2,4-DCP on the M-DF-RGO hybrid was performed under various conditions, with respect to initial chlorophenol concentration, pH, and contact time. The results suggest that the adsorption of 4-CP and 2,4-DCP onto the M-DF-RGO hybrid is strongly dependent on pH and weakly dependent on contact time. In addition, the adsorption isotherm of 4-CP and 2,4-DCP on the M-DF-RGO hybrid fits the Freundlich model well and the adsorption capacities of 4-CP and 2,4-DCP on M-DF-RGO reached 55.09 and 127.33 mg g-1, respectively, at pH 6 and 25 °C. In this situation, intermolecular interactions including π-π interactions and hydrogen bonding are operative. The calculated results of density functional theory further demonstrate that 2,4-DCP molecules could be more easily absorbed than 4-CP molecules by the M-DF-RGO hybrid. Moreover, the M-DF-RGO hybrid could be easily separated by a magnetic separation process, and showed good recyclability of more than five cycles.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




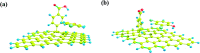
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of highly efficient adsorption of 2-chlorophenol onto ultrasonic graphene materials: Comparison and equilibrium.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016 Nov 1;481:168-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.049. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016. PMID: 27474817
-
Enhanced adsorption-coupled reduction of hexavalent chromium by 2D poly(m-phenylenediamine)-functionalized reduction graphene oxide.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Oct;26(30):31099-31110. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06175-x. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31452128
-
Polyethylene glycol functionalized reduced graphene oxide coupled with zinc oxide composite adsorbent for removal of phenolic wastewater.Environ Res. 2022 Nov;214(Pt 3):114044. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114044. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35985491
-
Magnetic polyethyleneimine functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a novel magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of polar acidic herbicides in rice.Anal Chim Acta. 2017 Jan 1;949:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.11.016. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Anal Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 27876142
-
Magnetic polyethyleneimine functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a novel magnetic sorbent for the separation of polar non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in waters.Talanta. 2019 Jan 1;191:526-534. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Talanta. 2019. PMID: 30262094
References
-
- Matias T. Marques J. Quina M. J. Gando-Ferreira L. Valente A. J. M. Portugal A. Durães L. Colloids Surf., A. 2015;480:260–269. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.01.074. - DOI
-
- Yang Q. Gao M. Zang W. Colloids Surf., A. 2017;520:805–816. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.02.057. - DOI
-
- Ahmaruzzaman M. Gayatri S. L. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2011;56:3004–3016. doi: 10.1021/je100937r. - DOI
-
- Dehghani M. H. Mostofi M. Alimohammadi M. McKay G. Yetilmezsoy K. Albadarin A. B. Heibati B. AlGhouti M. Mubarak N. M. Sahu J. N. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016;35:63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2015.12.010. - DOI
-
- Strachowski P. Bystrzejewski M. Colloids Surf., A. 2015;467:113–123. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.11.044. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

