Monascus pigment rubropunctatin derivative FZU-H reduces Aβ(1-42)-induced neurotoxicity in Neuro-2A cells
- PMID: 35539257
- PMCID: PMC9080402
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02365d
Monascus pigment rubropunctatin derivative FZU-H reduces Aβ(1-42)-induced neurotoxicity in Neuro-2A cells
Abstract
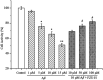
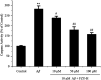
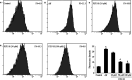
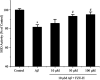
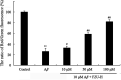
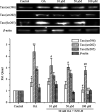
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an extremely complex disease, characterized by several pathological features including oxidative stress and amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation. Blockage of Aβ-induced injury has emerged as a potential therapeutic approach for AD. Our previous efforts resulted in the discovery of Monascus pigment rubropunctatin derivative FZU-H with potential neuroprotective effects. This novel lead compound significantly diminishes toxicity induced by Aβ(1-42) in Neuro-2A cells. Our further mechanism investigation revealed that FZU-H inhibited Aβ(1-42)-induced caspase-3 protein activation and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. In addition, treatment of FZU-H was proven to attenuate Aβ(1-42)-induced cell redox imbalance and Tau hyperphosphorylation which caused by okadaic acid in Neuro-2A cells. These results indicated that FZU-H shows promising neuroprotective effects for AD.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deciphering the anti-apoptotic potential of α-bisabolol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles against Aβ induced neurotoxicity in Neuro-2a cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Jun;190:110948. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110948. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 32160583
-
Monascus Pigment Rubropunctatin: A Potential Dual Agent for Cancer Chemotherapy and Phototherapy.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Mar 30;64(12):2541-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05343. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 26953890
-
Phytol loaded PLGA nanoparticles regulate the expression of Alzheimer's related genes and neuronal apoptosis against amyloid-β induced toxicity in Neuro-2a cells and transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans.Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Feb;136:110962. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.110962. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31734340
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Are N- and C-terminally truncated Aβ species key pathological triggers in Alzheimer's disease?J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 5;293(40):15419-15428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R118.003999. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30143530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eco-Friendly Green Synthesis of Rubropunctatin Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;12(22):4052. doi: 10.3390/nano12224052. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432337 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

