Liposuction and Controlled Compression Therapy Reduce the Erysipelas Incidence in Primary and Secondary Lymphedema
- PMID: 35539287
- PMCID: PMC9076442
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004314
Liposuction and Controlled Compression Therapy Reduce the Erysipelas Incidence in Primary and Secondary Lymphedema
Abstract
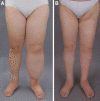
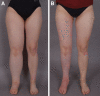
Background: Skin infections are a recurring problem for people with lymphedema, and lymphedema has been proven to be the single most important risk factor for developing erysipelas in the leg. This study aimed to determine whether liposuction for late-stage lymphedema reduces the rate of erysipelas in lower extremity lymphedema.
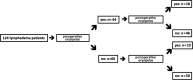
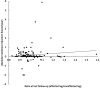
Methods: One-hundred twenty-four patients with a median age of 49 years who had liposuction and controlled compression therapy for lower extremity lymphedema were included. Excess volumes were calculated before and after surgery. Median preoperative and postoperative patient years at risk were 11 and 5 years, respectively.
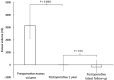
Results: With a total of 1680 preoperative person years at risk and 335 bouts of erysipelas experienced in 64 patients, the preoperative incidence rate was 0.20 bouts per person per year, and the period prevalence was 52%. Postoperatively, the patients were followed over a total of 763 person years at risk, and 28 patients experienced a total of 53 bouts of erysipelas, resulting in a postoperative incidence rate of 0.07 bouts per person per year, and a period prevalence of 23%. This represents a 65% decrease in the erysipelas incidence rate (P < 0.001). The preoperative median excess volume of 3158 ml was reduced with a median of 100% (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Liposuction and controlled compression therapy significantly reduce the risk for erysipelas in lower extremity lymphedema and completely reduces the excess volume. This finding is similar to our previous research including patients with upper extremity lymphedema.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined Surgical Treatment for Chronic Upper Extremity Lymphedema Patients: Simultaneous Lymph Node Transfer and Liposuction.Ann Plast Surg. 2019 Sep;83(3):308-317. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001828. Ann Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31008792
-
Liposuction of Postmastectomy Arm Lymphedema Decreases the Incidence of Erysipelas.Lymphology. 2016 Jun;49(2):85-92. Lymphology. 2016. PMID: 29906366
-
Complete Reduction of Leg Lymphedema after Liposuction: A 5-Year Prospective Study in 67 Patients without Recurrence.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023 Dec 7;11(12):e5429. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005429. eCollection 2023 Dec. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023. PMID: 38074499 Free PMC article.
-
Liposuction in Lymphedema Treatment.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2016 Jan;32(1):56-65. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1549158. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2016. PMID: 25893630 Review.
-
[Treatment of limbs lymphedema].Presse Med. 2010 Dec;39(12):1315-23. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2009.12.011. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Presse Med. 2010. PMID: 20850261 Review. French.
Cited by
-
[Application efficacy of lymph pads in complete decongestive therapy after lymphatico-venous anastomosis combined with liposuction in patients with lower limb lymphedema].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 20;41(6):552-558. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20241209-00481. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40588403 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Lymphatic venous anastomosis and complex decongestive therapy for lymphoedema: randomized clinical trial.Br J Surg. 2024 Jan 3;111(1):znad372. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znad372. Br J Surg. 2024. PMID: 37997932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Liposuction for Advanced Lymphedema in a Multidisciplinary Team Setting in Australia: 5-Year Follow-Up.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2024 Feb 1;153(2):482-491. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010612. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2024. PMID: 37114928 Free PMC article.
-
[An overview of integrated surgical management for secondary lower limb lymphedema guided by algorithms].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 20;41(6):516-524. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20250217-00067. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40480841 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Szuba A, Rockson SG. Lymphedema: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Vasc Med. 1998;3:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Trinh L, Peterson P, Brorson H, et al. . Assessment of subfascial muscle/water and fat accumulation in lymphedema patients using magnetic resonance imaging. Lymphat Res Biol. 2019;17:340–346. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
