Amine-functionalized MIL-53(Al) with embedded ruthenium nanoparticles as a highly efficient catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane
- PMID: 35539406
- PMCID: PMC9079245
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra01507d
Amine-functionalized MIL-53(Al) with embedded ruthenium nanoparticles as a highly efficient catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane
Abstract
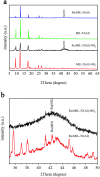
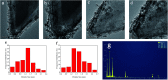
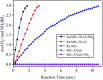
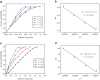
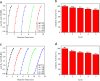
Well-dispersed ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru NPs) are immobilized within the pores of amine-functionalized MIL-53 via an in situ impregnation-reduction method. The resulting Ru/MIL-53(Al)-NH2 catalyst exhibits superior catalytic performance for the dehydrogenation of ammonia borane (AB) at ambient temperature relative to the Ru/MIL-53(Al) catalyst; it has a turnover frequency (TOF) of 287 mol H2 min-1 (mol Ru)-1 and an activation energy (E a) of 30.5 kJ mol-1. The amine groups present in the MIL-53(Al)-NH2 framework facilitate the formation and stabilization of ultra-small Ru NPs by preventing their aggregation. Additionally, the Ru/MIL-53(Al)-NH2 catalyst exhibits satisfactory durability and reusability: 72.4% and 86.3% of the initial catalytic activity was maintained after the fifth successive cycle of the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of AB in the two respective tests.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Jena P. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011;2:206–211. doi: 10.1021/jz1015372. - DOI
-
- Roy B. Manna J. Sharma P. J. Alloys Compd. 2015;645:234–238. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.046. - DOI
-
- Wang H. Zhou L. Han M. Tao Z. Cheng F. Chen J. J. Alloys Compd. 2015;651:382–388. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.08.139. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

