Underdiagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis by ECG and echocardiography in cases of extracardiac sarcoidosis
- PMID: 35539437
- PMCID: PMC9081545
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00516-2021
Underdiagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis by ECG and echocardiography in cases of extracardiac sarcoidosis
Abstract
Background: Although screening with 12-lead electrocardiography and transthoracic echocardiography for cardiac involvement has been recommended for patients with biopsy-proven extracardiac sarcoidosis, cardiac sarcoidosis has been reported even in patients with normal electrocardiography and echocardiography findings. We investigated the prevalence and characteristics of these patient cohorts.
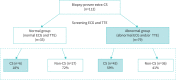
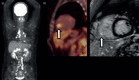
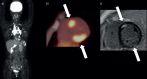
Methods: We studied 112 consecutive patients (age, 55±17 years, 64% females) with biopsy-proven extracardiac sarcoidosis who had undergone 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging for cardiac sarcoidosis evaluation. The patients were categorised as those showing normal findings both in electrocardiography and transthoracic echocardiography (normal group) and those showing abnormal findings in one or both examinations (abnormal group).
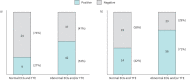
Results: 33 (29%) and 79 (71%) patients were categorised into the normal and abnormal groups, respectively, of which 6 (18%) and 43 (54%) patients, respectively, were diagnosed with cardiac sarcoidosis (p<0.01). Of these six patients in the normal group, two with multiple-organ sarcoidosis showed clinical deterioration of cardiac involvement and required steroid therapy; three with small cardiac involvement showed natural remission over follow-up assessments; and one underwent steroid therapy and showed an improvement in the left ventricular ejection fraction to within normal limits.
Conclusions: The prevalence of cardiac sarcoidosis in patients with biopsy-proven extracardiac sarcoidosis and normal electrocardiography and transthoracic echocardiography findings was ∼20%. Electrocardiography and transthoracic echocardiography may not detect cardiac sarcoidosis in patients without conduction and morphological abnormalities. However, some of these patients may subsequently show clinically manifested cardiac sarcoidosis. Physicians should be mindful of this population.
Copyright ©The authors 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
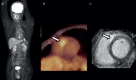
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the interventricular septum is associated with atrioventricular block in patients with suspected cardiac involvement sarcoidosis.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013 Oct;40(10):1558-66. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2460-5. Epub 2013 May 29. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23715906
-
Electrophysiologic testing for diagnostic evaluation and risk stratification in patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis with preserved left and right ventricular systolic function.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019 Oct;30(10):1939-1948. doi: 10.1111/jce.14058. Epub 2019 Jul 23. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31257683
-
The Utility of Whole Body 18F-FDG PET-CT in Diagnosing Isolated Cardiac Sarcoidosis: The Western Australian Cardiac Sarcoid Study.Heart Lung Circ. 2020 Jan;29(1):e1-e6. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Heart Lung Circ. 2020. PMID: 31501049
-
[Cardiac sarcoidosis: diagnostics, treatment and follow-up].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2018 Mar 27;44(261):124-129. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2018. PMID: 29601561 Review. Polish.
-
The Role of Echocardiography in the Contemporary Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Jul 29;13(8):1653. doi: 10.3390/life13081653. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629510 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contemporary Diagnostics of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: The Importance of Multimodality Imaging.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 26;14(17):1865. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14171865. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcoid heart disease and imaging.Heart Rhythm O2. 2023 Nov 19;5(1):50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.hroo.2023.11.012. eCollection 2024 Jan. Heart Rhythm O2. 2023. PMID: 38312203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac sarcoidosis: phenotypes, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.Eur Heart J. 2023 May 1;44(17):1495-1510. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad067. Eur Heart J. 2023. PMID: 36924191 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic values of delayed additional FDG PET/CT scan in the evaluation of cardiac sarcoidosis.Ann Nucl Med. 2023 Oct;37(10):535-540. doi: 10.1007/s12149-023-01855-8. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Ann Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37418117
-
Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Clinical Insights, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Feb 21;26(2):26605. doi: 10.31083/RCM26605. eCollection 2025 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40026523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Terasaki F, Yoshinaga K. New guidelines for diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis. Ann Nucl Cardiol 2017; 3: 42–45. doi:10.17996/anc.17-00042 - DOI
-
- Mc Ardle BA, Birnie DH, Klein R, et al. . Is there an association between clinical presentation and the location and extent of myocardial involvement of cardiac sarcoidosis as assessed by 1⁸F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2013; 6: 617–626. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.000289 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
