Simple and rapid monitoring of doxorubicin using streptavidin-modified microparticle-based time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay
- PMID: 35539486
- PMCID: PMC9080157
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra01807c
Simple and rapid monitoring of doxorubicin using streptavidin-modified microparticle-based time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay
Abstract
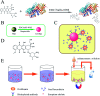
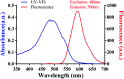
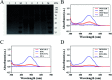
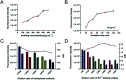
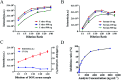
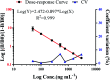
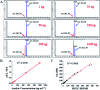
Developing a simple analytical method suitable for therapeutic drug monitoring in a clinical setting is key to establishing guidelines on accurate dose administration and the advancement of precision medicine. We devised a simple rapid analytical method through the combination of streptavidin-modified microparticles and a time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay for therapeutic drug monitoring. The analytical performance of this method was investigated and validated using clinical samples. By determination of doxorubicin concentration, the proposed assay has shown a satisfactory linear range of detection (3.8-3000 ng mL-1) with a limit of detection of 3.8 ng mL-1 and an IC50 of 903.9 ng mL-1. The intra and inter-assay coefficients of variation were 4.12-5.72% and 5.48-6.91%, respectively, and the recovery was acceptable. The applicability of the proposed assay was assessed by comparing the determined results with those measured by LC-MS/MS, presenting a satisfactory correlation (R 2 = 0.9868). The proposed assay, which shows satisfactory analytical performance, has great potential for application in the field of TDM in the future.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Galpin A. J. Evans W. E. Clin. Chem. 1993;39:2419–2430. - PubMed
-
- Tangden T. Ramos Martin V. Felton T. W. Nielsen E. I. Marchand S. Bruggemann R. J. Bulitta J. B. Bassetti M. Theuretzbacher U. Tsuji B. T. Wareham D. W. Friberg L. E. De Waele J. J. Tam V. H. Roberts J. A. t. P. Infection Section for the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine M. Pharmacodynamics Study Group of the European Society of Clinical t. I. S. o. A.-I. P. Infectious Diseases M. the Critically Ill Patients Study Group of European Society of Clinical and D. Infectious Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:1021–1032. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4780-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

