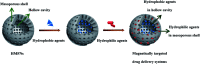
Magnetically targeted co-delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs with hollow mesoporous ferrite nanoparticles
- PMID: 35539487
- PMCID: PMC9080009
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02343c
Magnetically targeted co-delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs with hollow mesoporous ferrite nanoparticles
Abstract
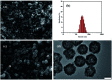
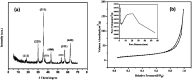
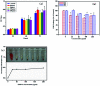
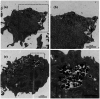
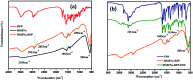
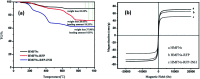
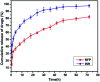
A magnetically targeted drug delivery system (DDS) is developed to solve the delivery problem of hydrophobic drugs by using hollow mesoporous ferrite nanoparticles (HMFNs). The HMFNs are synthesized by a one-pot hydrothermal method based on the Ostwald ripening process. The biocompatibility of the synthesized HMFNs was determined by MTT assay, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage assay and hemolyticity against rabbit red blood cells. Moreover, Prussian blue staining and bio-TEM observations showed that the cell uptake of nanocarriers was in a dose and time-dependent manner, and the nanoparticles accumulate mostly in the cytoplasm. A typical highly hydrophobic anti-tuberculosis drug, rifampin (RFP) was loaded into HMFNs using supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) impregnation, and the drug loading amount reached as high as 18.25 wt%. In addition, HMFNs could co-encapsulate and co-deliver hydrophobic (RFP) and hydrophilic (isoniazide, INH) drugs simultaneously. The in vitro release tests demonstrated extra sustained co-release profiles of rifampicin and isoniazide from HMFNs. Based on this novel design strategy, the co-delivery of drugs in the same carrier enables a drug delivery system with efficient enhanced chemotherapeutic effect.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced Antimalarial Efficacy Obtained by Targeted Delivery of Artemisinin in Heparin-Coated Magnetic Hollow Mesoporous Nanoparticles.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Jan 13;13(1):287-297. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c20070. Epub 2020 Dec 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33356111
-
A mesoporous silica nanoparticulate/β-TCP/BG composite drug delivery system for osteoarticular tuberculosis therapy.Biomaterials. 2011 Mar;32(7):1986-95. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.11.025. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21163519
-
Optical imaging and anticancer chemotherapy through carbon dot created hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jun;55:466-480. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.054. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28373086
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported nanocarriers with enhanced drug loading, encapsulation stability, and targeting efficiency.Biomater Sci. 2022 Mar 15;10(6):1448-1455. doi: 10.1039/d2bm00010e. Biomater Sci. 2022. PMID: 35229845 Review.
-
Hollow Inorganic Nanoparticles as Efficient Carriers for siRNA Delivery: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(29):4310-28. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150901103937. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26323421 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Mediated Co-Delivery System: A Promising Strategy in Medical and Agricultural Field.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5121. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065121. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: a review.RSC Adv. 2019 Feb 25;9(12):6460-6481. doi: 10.1039/c8ra08088g. eCollection 2019 Feb 22. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35518468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pNIPAm-Based pH and Thermoresponsive Copolymer Hydrogel for Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Drug Delivery.Gels. 2024 Mar 7;10(3):184. doi: 10.3390/gels10030184. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38534602 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Plant Viral Nanoparticles in Cancer Biotherapy-A Review.Viruses. 2025 Feb 1;17(2):218. doi: 10.3390/v17020218. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40006973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Resveratrol Within Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Prostate Cancer Therapy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Sep 18;7:225. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00225. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31620434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peppas N. A. Hilt J. Z. Khademhosseini A. Langer R. Adv. Mater. 2006;18:1345–1360. doi: 10.1002/adma.200501612. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

