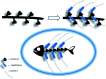
Poly-histidine grafting leading to fishbone-like architectures
- PMID: 35539867
- PMCID: PMC9078612
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00315g
Poly-histidine grafting leading to fishbone-like architectures
Abstract
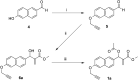
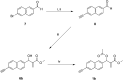
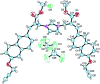
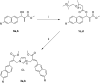
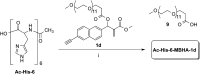
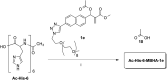
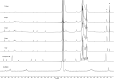
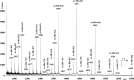
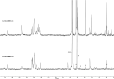
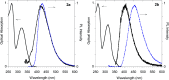
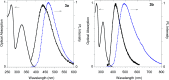
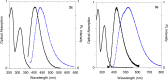
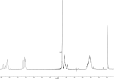
A small series of Morita-Baylis-Hillman adduct (MBHA) derivatives was synthesized and made to react with imidazole, N-acetylhistidine, and N-acetylhexahistidine as models of poly-histidine derivatives. Intriguingly, the reaction of MBHA derivatives 1a and b with imidazole in acetonitrile-phosphate buffered saline (PBS) gave the imidazolium salt biadducts 3a and b as the main reaction products. These results were confirmed by experiments performed with N-acetylhistidine and 1b and suggested the possible occurrence of these structures in the products of poly-histidine labeling with MBHA derivatives 1a and b. These compounds were then transformed into the corresponding water-soluble derivatives 1c-e by introducing oligo(ethylene glycol) chains and their reactivity was evaluated in preliminary experiments with imidazole and then with N-acetylhexahistidine in PBS. The structure of polymeric materials Ac-His-6-MBHA-1d and Ac-His-6-MBHA-1e obtained using ten-fold excesses of compounds 1d and e was investigated using mass spectrometry, NMR spectroscopy, and photophysical studies, which suggested the presence of biadduct residues in both polymeric materials. These results provide the basis for the preparation of fishbone-like polymer brushes, the characterization of their properties, and the exploration of their potential applications in different fields of science such as in vivo fluorogenic labeling, fluorescence microscopy, protein PEGylation, up to the production of smart materials and biosensors.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Reactivity of Oligo(ethylene glycol)-Tethered Morita-Baylis-Hillman Dimers in the Formation of Macrocyclic Structures Showing Remarkable Cytotoxicity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 27;18(4):473. doi: 10.3390/ph18040473. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283910 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivity of a Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adduct Derivative Bearing a Triphenylamine Moiety with Lysine Models.Chem Asian J. 2024 Oct 16;19(20):e202400617. doi: 10.1002/asia.202400617. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Chem Asian J. 2024. PMID: 39041884
-
Synthesis, Cytotoxic Activity on Leukemia Cell Lines and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships (QSAR) Studies of Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adducts.Med Chem. 2016;12(7):602-612. doi: 10.2174/1573406412666160506150924. Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27150963
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
"Polymeromics": Mass spectrometry based strategies in polymer science toward complete sequencing approaches: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2014 Jan 15;808:56-69. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.027. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Anal Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24370093 Review.
Cited by
-
Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adduct Chemistry as a Tool for the Design of Lysine-Targeted Covalent Ligands.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025 Feb 28;16(3):397-405. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00479. eCollection 2025 Mar 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40104796
-
Gene delivery by peptide-assisted transport.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Sep;7:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 30906908 Free PMC article.
-
A tri(ethylene glycol)-tethered Morita-Baylis-Hillman dimer in the formation of macrocyclic crown ether-paracyclophane hybrid structures.RSC Adv. 2023 Dec 11;13(51):35773-35780. doi: 10.1039/d3ra06792k. eCollection 2023 Dec 8. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38090072 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthopsin-Like Systems via Site-Specific Click-Functionalization of a Retinoic Acid Binding Protein.Chembiochem. 2022 Jan 5;23(1):e202100449. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100449. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 34647400 Free PMC article.
-
Solid-Phase Synthesized Copolymers for the Assembly of pH-Sensitive Micelles Suitable for Drug Delivery Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 May 24;12(11):1798. doi: 10.3390/nano12111798. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnard E. A. and Stein W. D., The Roles of Imidazole in Biological Systems, Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology, ed, F. F. Nord, Wiley, 2006, vol. 20; pp. 51–110 - PubMed
-
- Sundberd R. J. Martin R. B. Chem. Rev. 1974;74:471–517. doi: 10.1021/cr60290a003. - DOI
-
- Mavrogiorgis D. Bilalis P. Karatzas A. Skoulas D. Fotinogiannopoulou G. Iatrou H. Polym. Chem. 2014;5:6256–6278. doi: 10.1039/C4PY00687A. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

