Retracted Article: Linc00472 suppresses breast cancer progression and enhances doxorubicin sensitivity through regulation of miR-141 and programmed cell death 4
- PMID: 35539872
- PMCID: PMC9078624
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00296g
Retracted Article: Linc00472 suppresses breast cancer progression and enhances doxorubicin sensitivity through regulation of miR-141 and programmed cell death 4
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Linc00472 suppresses breast cancer progression and enhances doxorubicin sensitivity through regulation of miR-141 and programmed cell death 4.RSC Adv. 2021 Feb 2;11(11):5895. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90067f. eCollection 2021 Feb 2. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35427065 Free PMC article.
Abstract
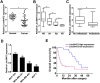
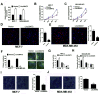
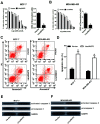
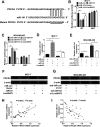
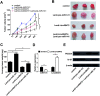
The existence of drug resistance strikingly hampers the therapy of many malignancies, including breast cancer. Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) have been reported to participate in the regulation of various biological processes associated with cancer progression. Whereas, the role of linc00472 in breast cancer pathogenesis and doxorubicin (ADR) resistance have not been well elucidated. In the present study, it is found that linc00472 expression was decreased in breast cancer tissues and cells. Moreover, higher linc00472 expression was positively associated with favorable disease status and prognosis for breast cancer patients. Functional analyses revealed that linc00472 overexpression suppressed proliferation and invasion, facilitated apoptosis and enhanced ADR sensitivity in breast cancer cells. Mechanistic studies discovered that linc00472 acted as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) of miR-141 to sequester miR-141 from its target mRNA PDCD4 (programmed cell death 4). Furthermore, the inhibition effect of linc00472 on breast cancer cell progression and ADR resistance could be partly abrogated by miR-141 up-regulation or PDCD4 knockdown. In vivo assays also demonstrated that linc00472 hindered tumor growth by suppressing miR-141 expression and enhancing PDCD4 expression. In conclusion, linc00472 blocked breast cancer progression and induced ADR sensitivity through regulation of miR-141 and PDCD4, highlighting a potential therapeutic strategy for breast cancer patients.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Cardoso F. Castiglione M. Group E. G. W. Ann. Oncol. 2009;22:15–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

