An evolutionary explanation for antibiotics' association with increased colon cancer risk
- PMID: 35539898
- PMCID: PMC9081870
- DOI: 10.1093/emph/eoac018
An evolutionary explanation for antibiotics' association with increased colon cancer risk
Abstract
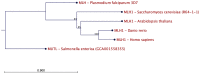
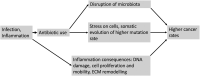
: More than 10 studies have confirmed the association of antibiotic overuse with colorectal cancer. The exact cause is unknown, but most authors hypothesize that disturbance of colon microbiota is the main culprit. In this commentary, an evolutionary explanation is proposed. It is well known that antibiotics can induce antibiotic resistance in bacteria through selection of mutators-DNA mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) strains. Mutators have an increased survival potential due to their high mutagenesis rate. Antibiotics can also cause stress in human cells. Selection of dMMR colon cells may be advantageous under this stress, mimicking selection of bacterial mutators. Concomitantly, mismatch repair deficiency is a common cause of cancer, this may explain the increased cancer risk after multiple cycles of oral antibiotics. This proposed rationale is described in detail, along with supporting evidence from the peer-reviewed literature and suggestions for testing hypothesis validity. Treatment schemes could be re-evaluated, considering toxicity and somatic selection mechanisms.
Lay summary: The association of antibiotics with colon cancer is well established but of unknown cause. Under an evolutionary framework, antibiotics may select for stress-resistant cancerous cells that lack mechanisms for DNA mismatch repair (MMR). This mimics the selection of antibiotic resistant 'mutators'-MMR-deficient micro-organisms-highly adaptive due to their increased mutagenesis rate.
Keywords: DNA repair; MLH1; MSH2; adaptation; cancer evolution; natural selection.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Foundation for Evolution, Medicine, and Public Health.
Figures
References
-
- Kilkkinen A, Rissanen H, Klaukka T. et al. Antibiotic use predicts an increased risk of cancer. Int J Cancer 2008;123:2152–5. - PubMed
-
- Wang JL, Chang CH, Lin JW. et al. Infection, antibiotic therapy and risk of colorectal cancer: a nationwide nested case-control study in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Cancer 2014;135:956–67. - PubMed
-
- Boursi B, Haynes K, Mamtani R. et al. Impact of antibiotic exposure on the risk of colorectal cancer. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2015;24:534–42. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Haines C, Watson AJM. et al. Oral antibiotic use and risk of colorectal cancer in the United Kingdom, 1989-2012: a matched case-control study. Gut 2019;68:1971–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

