Enhancing the mechanical performance of poly(ether ether ketone)/zinc oxide nanocomposites to provide promising biomaterials for trauma and orthopedic implants
- PMID: 35539979
- PMCID: PMC9083298
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra01736k
Enhancing the mechanical performance of poly(ether ether ketone)/zinc oxide nanocomposites to provide promising biomaterials for trauma and orthopedic implants
Abstract
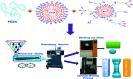
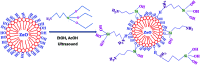
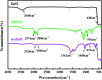
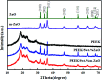
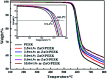
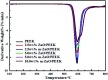
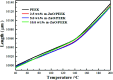
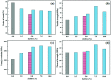
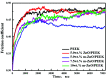
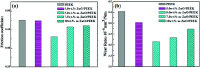
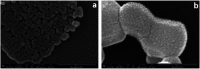
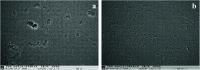
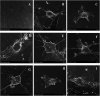
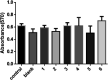
Poly(ether ether ketone)/zinc oxide (PEEK/ZnO) composites were manufactured by using the injection molding technique. Before blending with the PEEK resin matrix, some ZnO nanoparticles were modified by γ-aminopropyltriethoxylsilane (APTES). The effect of surface modification of ZnO nanoparticles by amino groups and Si-O bonds was investigated. PEEK/ZnO composites were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis, and X-ray diffraction. The scanning electron micrographs showed that ZnO nanoparticles were encapsulated in the PEEK phase; within this phase, the nanoparticles were homogeneously dispersed. Mechanical and tribological properties were measured by tensile strength, flexural strength, coefficient of friction, and wear rate. It was shown that the interfacial compatibility between ZnO nanoparticles and PEEK matrix was significantly enhanced due to the amino and Si-O bonds decorated on the ZnO nanoparticles. More importantly, the thermal stability of PEEK improved upon the incorporation of ZnO nanoparticles into this matrix. Cell viability studies with mouse osteoblasts demonstrated that cell growth on PEEK and PEEK/ZnO was significantly enhanced. On the basis of the obtained results, PEEK/ZnO composites are recommended as promising candidates for orthopaedic materials and trauma implants.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of Multifunctional Materials Based on Poly(ether ether ketone) with Improved Biological Performances for Dental Applications.Materials (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;14(4):1047. doi: 10.3390/ma14041047. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672249 Free PMC article.
-
Poly (Ether-Ether-Ketone) for Biomedical Applications: From Enhancing Bioactivity to Reinforced-Bioactive Composites-An Overview.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;15(2):373. doi: 10.3390/polym15020373. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of nanocomposites reinforced with carboxylated poly(ether ether ketone) grafted to zinc oxide with superior antibacterial properties.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Mar 12;6(5):3729-41. doi: 10.1021/am500171x. Epub 2014 Feb 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 24552261
-
Development and characterization of novel poly(ether ether ketone)/ZnO bionanocomposites.J Mater Chem B. 2014 May 28;2(20):3065-3078. doi: 10.1039/c3tb21800g. Epub 2014 Apr 14. J Mater Chem B. 2014. PMID: 32261682
-
An overview of the tribological and mechanical properties of PEEK and CFR-PEEK for use in total joint replacements.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023 Sep;145:105974. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.105974. Epub 2023 Jun 25. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023. PMID: 37429179 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoformulation Composed of Ellagic Acid and Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Inactivates DNA and RNA Viruses.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 16;13(12):2174. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122174. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959455 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Class of Cost Effective and High Performance Composites Based on Terephthalate Salts Reinforced Polyether Ether Ketone.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Dec 14;11(12):2097. doi: 10.3390/polym11122097. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31847354 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Multifunctional Materials Based on Poly(ether ether ketone) with Improved Biological Performances for Dental Applications.Materials (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;14(4):1047. doi: 10.3390/ma14041047. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672249 Free PMC article.
-
Biologically Modified Polyether Ether Ketone as Dental Implant Material.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Dec 18;8:620537. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.620537. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33392178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly (Ether-Ether-Ketone) for Biomedical Applications: From Enhancing Bioactivity to Reinforced-Bioactive Composites-An Overview.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;15(2):373. doi: 10.3390/polym15020373. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679253 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hou X. Hu Y. Hu X. Jiang D. Poly(ether ether ketone) composites reinforced by graphene oxide and silicon dioxide nanoparticles: mechanical properties and sliding wear behavior. High Perform. Polym. 2017;30(4):406–417. doi: 10.1177/0954008317701549. - DOI
-
- Hoskins T. J. Dearn K. D. Chen Y. K. Kukureka S. N. The wear of PEEK in rolling – sliding contact – simulation of polymer gear applications. Wear. 2014;309:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2013.09.014. - DOI
-
- Li F. Hu Y. Hou X. Hu X. Jiang D. Thermal, mechanical, and tribological properties of short carbon fibers/PEEK composites. High Perform. Polym. 2017;30(6):657–666. doi: 10.1177/0954008317715313. - DOI
-
- Amanat N. Chaminade C. Grace J. et al., Transmission laser welding of amorphous and semi-crystalline poly-ether-ether-ketone for applications in the medical device industry. Mater. Des. 2010;31(10):4823–4830. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.04.051. - DOI
-
- Hu Y. Hou X. Hu X. Jiang D. Improvement in the Mechanical and Friction Performance of Poly(ether ether ketone) Composites by Addition of Modificatory Short Carbon Fibers and Zinc Oxide. High Perform. Polym. 2017;30(6):643–656. doi: 10.1177/0954008317723445. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

