Flavin-mediated extracellular electron transfer in Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus cereus DIF1 and Rhodococcus ruber DIF2
- PMID: 35540069
- PMCID: PMC9076428
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra08045g
Flavin-mediated extracellular electron transfer in Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus cereus DIF1 and Rhodococcus ruber DIF2
Abstract
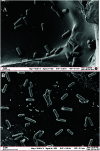
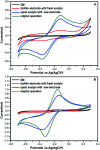
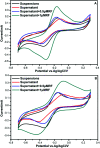
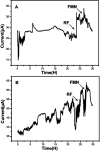
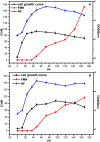
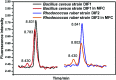
Flavin-mediated extracellular electron transfer was studied in two Gram-positive bacteria: Bacillus cereus strain DIF1 and Rhodococcus ruber strain DIF2. The electrochemical activities of these strains were confirmed using amperometric I-t curves and cyclic voltammetry (CV). Spent anodes with biofilms in fresh anolytes showed no redox peaks, while new anodes in the spent broth showed relative redox peaks using CV measurements, indicating the presence of a redox electron mediator secreted by bacteria. Adding riboflavins (RF) and flavin mononucleotide (FMN) improved the electron transfer of the microbial fuel cells inoculated with the two strains. The redox peaks indicated that flavins existed in the anolyte, and HPLC analysis showed that RF and FMN were secreted by the two bacterial strains. The concentration of RF increased until the bacteria grew to the log phase in microbial fuel cells. The concentration of RF decreased and that of FMN increased after the log phase. The two strains secreted FMN only in the microbial fuel cell. These results confirmed that the electrochemical activity mediated by flavins and FMN is essential in the extracellular electron transfer process in the strains DIF1 and DIF2.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Neal A. L. Rosso K. M. Geesey G. G. Gorby Y. A. Little B. J. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2003;67(23):4489–4503. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00386-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

