On the synergy between silver nanoparticles and doxycycline towards the inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus growth
- PMID: 35540305
- PMCID: PMC9081745
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02176g
On the synergy between silver nanoparticles and doxycycline towards the inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus growth
Abstract
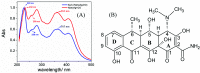
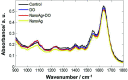
In a previous paper (RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 66886-66893), we showed that the combination of silver nanoparticles (NanoAg) with doxycycline (DO) culminated in an increased bactericidal activity towards E. coli. Herein we further investigated the metabolic changes that occurred on Staphylococcus aureus upon exposure to NanoAg with the help of attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) coupled with multivariate data analysis. It has been discovered that the combination of DO with NanoAg produced metabolic changes in S. aureus that were not simply the overlap of the treatments with DO and NanoAg separately. Our results suggest that DO and NanoAg act synergistically to impede protein synthesis by the bacteria.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial potency of differently coated 10 and 50 nm silver nanoparticles against clinically relevant bacteria Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 Oct 1;170:401-410. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.06.027. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 29945052
-
Elemental profiles of freshwater mussels treated with silver nanoparticles: A metallomic approach.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;188:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 19. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27211012
-
Antibacterial properties and compressive strength of new one-step preparation silver nanoparticles in glass ionomer cements (NanoAg-GIC).J Dent. 2018 Feb;69:102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 16. J Dent. 2018. PMID: 29253621
-
Colorimetric detection of Hg(II) by γ-aminobutyric acid-silver nanoparticles in water and the assessment of antibacterial activities.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 Apr 15;251:119433. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119433. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 33465574
-
In Ovo Administration of Silver Nanoparticles and/or Amino Acids Influence Metabolism and Immune Gene Expression in Chicken Embryos.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Apr 27;16(5):9484-503. doi: 10.3390/ijms16059484. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25923079 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Reducing the effective dose of doxycycline using chitosan silver nanocomposite as a carriers on gram positive and gram-negative bacteria.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27819. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78326-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537761 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effect of Silver Nanoparticles with Antibiotics for Eradication of Pathogenic Biofilms.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(14):1884-1903. doi: 10.2174/0113892010279217240102100405. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38231054
-
Identification of resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy and multivariate analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 3;10(1):12994. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70033-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32747745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rastogi S. K. Rutledge V. J. Gibson C. Newcombe D. A. Branen J. R. Branen A. L. Ag colloids and Ag clusters over EDAPTMS-coated silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli. Nanomedicine. 2011;7:305–314. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2010.11.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

