Sonochemical preparation of alumina-spheres loaded with Pd nanoparticles for 2-butyne-1,4-diol semi-hydrogenation in a continuous flow microwave reactor
- PMID: 35540310
- PMCID: PMC9078474
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00331a
Sonochemical preparation of alumina-spheres loaded with Pd nanoparticles for 2-butyne-1,4-diol semi-hydrogenation in a continuous flow microwave reactor
Abstract
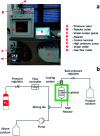
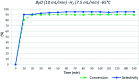
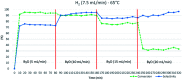
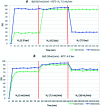
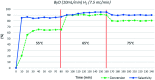
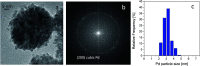
A novel protocol for microwave-assisted alkyne semi-hydrogenation under heterogeneous catalysis in a continuous flow reactor is reported herein. This challenging task has been accomplished using a multifaceted strategy which includes the ultrasound-assisted preparation of Pd nanoparticles (average Ø 3.0 ± 0.5 nm) that were synthesized on the μ-metric pores of sintered alumina spheres (Ø 0.8 mm) and a continuous flow reaction under H2 (flow rate 7.5 mL min-1) in a microwave reactor (counter-pressure 4.5 bar). The semi-hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol in ethanol was chosen as a model reaction for the purposes of optimization. The high catalyst efficiency of the process, in spite of the low Pd loading (Pd content 111.15 mg kg-1 from ICP-MS), is due to the pivotal role of ultrasound in generating a regular distribution of Pd nanoparticles across the entire support surface. Ultrasound promotes the nucleation, rather than the growth, of crystalline Pd nanoparticles and does so within a particularly narrow Gaussian size distribution. High conversion (>90.5%) and selectivity to (Z)-2-butene-1,4-diol (95.20%) have been achieved at an alkyne solution flow rate of 10 mL min-1. The lead-free, alumina-stabilized Pd catalyst was fully characterized by TEM, HR-TEM, EDX, IR, XRPD and AAS. Highly dispersed Pd nanoparticles have proven themselves to be stable under the reaction conditions employed. The application of the method is subject to the dielectric properties of substrates and solvents, and is therefore hardly applicable to apolar alkynes. Considering the small volume of the reaction chamber, microwave-assisted flow hydrogenation has proven itself to be a safe procedure and one that is suitable for further scaling up to industrial application.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

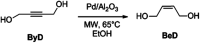
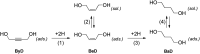

Similar articles
-
Ultrasonically improved semi-hydrogenation of alkynes to (Z-)alkenes over novel lead-free Pd/Boehmite catalysts.Ultrason Sonochem. 2017 Mar;35(Pt B):664-672. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 May 20. Ultrason Sonochem. 2017. PMID: 27255737
-
Solvent-Free Hydrogenation of Squalene Using Parts per Million Levels of Palladium Supported on Carbon Nanotubes: Shift from Batch Reactor to Continuous-Flow System.ChemSusChem. 2022 Oct 10;15(19):e202200916. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202200916. Epub 2022 Aug 25. ChemSusChem. 2022. PMID: 35880580 Free PMC article.
-
Palladium Nanoparticles Supported on Cellulosic Paper as Multifunctional Catalyst for Coupling and Hydrogenation Reactions.Chem Asian J. 2022 Feb 1;17(3):e202101195. doi: 10.1002/asia.202101195. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Chem Asian J. 2022. PMID: 34970847
-
Selective semihydrogenation of alkynes on shape-controlled palladium nanocrystals.Chem Asian J. 2013 May;8(5):919-25. doi: 10.1002/asia.201201166. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Chem Asian J. 2013. PMID: 23468235
-
Synthesis of Alkanethiolate-Capped Metal Nanoparticles Using Alkyl Thiosulfate Ligand Precursors: A Method to Generate Promising Reagents for Selective Catalysis.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 May 18;8(5):346. doi: 10.3390/nano8050346. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29783714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pyrene Functionalized Highly Reduced Graphene Oxide-palladium Nanocomposite: A Novel Catalyst for the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction in Water.Front Chem. 2022 Apr 29;10:872366. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.872366. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35572099 Free PMC article.
-
Sonochemical synthesis of aluminium and aluminium hybrids for remediation of toxic metals.Ultrason Sonochem. 2021 Jan;70:105299. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105299. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021. PMID: 32781427 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave-Assisted Dehydrogenative Cross Coupling Reactions in γ-valerolactone with a Reusable Pd/β-cyclodextrin Crosslinked Catalyst.Molecules. 2019 Jan 14;24(2):288. doi: 10.3390/molecules24020288. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30646596 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Microwaves on Organic Synthesis and Strategies toward Flow Processes and Scaling Up.J Org Chem. 2021 Oct 15;86(20):13857-13872. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00865. Epub 2021 Jun 14. J Org Chem. 2021. PMID: 34125541 Free PMC article.
-
From Batch to the Semi-Continuous Flow Hydrogenation of pNB, pNZ-Protected Meropenem.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 23;15(5):1322. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051322. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindlar H. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1952;35:446. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19520350205. - DOI
-
- Zhao M. Chem.–Asian J. 2016;11:461. doi: 10.1002/asia.201500939. - DOI - PubMed
- Delgado J. A. Benkirane O. Claver C. Curulla-Ferré D. Godard C. Dalton Trans. 2017;46:12381. doi: 10.1039/C7DT01607G. - DOI - PubMed
- Yin D. Li C. Ren H. Shekhah O. Liu J. Liang C. RSC Adv. 2017;7:1626. doi: 10.1039/C6RA25722D. - DOI
- Li H.-F. Zhang Q.-S. Pang Z.-B. Tian M. Gao P. Wang L.-L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016;27:1500. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2016.03.036. - DOI
- Yang S. Cao C. Peng L. Zhang J. Hanc B. Song W. Chem. Commun. 2016;52:3627. doi: 10.1039/C6CC00143B. - DOI - PubMed
- Yang J. Ma J.-J. Zhang D.-M. Xue T. Guan Y.-J. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016;27:1679. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2016.04.015. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

