Development of a bio-electrospray system for cell and non-viral gene delivery
- PMID: 35540421
- PMCID: PMC9078360
- DOI: 10.1039/c7ra12477e
Development of a bio-electrospray system for cell and non-viral gene delivery
Erratum in
-
Correction: Development of a bio-electrospray system for cell and non-viral gene delivery.RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 16;8(20):10735. doi: 10.1039/c8ra90023j. eCollection 2018 Mar 16. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35543981 Free PMC article.
Abstract
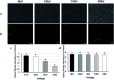
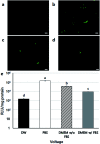
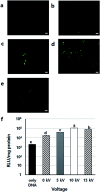
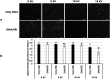
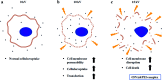
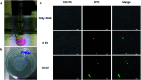
Bio-electrospray technology is a very attractive tool for preparing scaffolds and depositing desired solutions on various targets by electric force. In this study, we focused on the application of a bio-electrospray (BES) technique to spray cells on the target and to simultaneously deliver genetic constructs into the cells, called non-viral gene delivery-based bio-electrospray (NVG-BES). Using this method, we tried to harvest the electric charge produced during electrospray for the cellular internalization of cationic polymer/DNA nanoparticles as well as the delivery of living cells on the desired substrate. Furthermore, we optimized the voltage, culture medium and polymeric cationic charges for high transfection efficiency and cell viability during NVG-BES. As a result, the solutions used during the NVG-BES process played an important role in improving transfection efficiency. We determined that a voltage of 10 kV with PBS as the spraying solution showed high transfection efficiency, probably due to the facilitation of cationic polymer/DNA nanocomplexes in cellular internalization and their subsequent expression. In conclusion, NVG-BES, as a novel method, is expected to deliver genes to cells and simultaneously deliver transfected cells to any substrate or scaffold.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bio-electrospraying of human mesenchymal stem cells: An alternative for tissue engineering.Biomicrofluidics. 2013 Aug 29;7(4):44130. doi: 10.1063/1.4819747. eCollection 2013. Biomicrofluidics. 2013. PMID: 24404063 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric Nanoparticles in Gene Therapy: New Avenues of Design and Optimization for Delivery Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Apr 25;11(4):745. doi: 10.3390/polym11040745. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31027272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral vector mimicking and nucleus targeted nanoparticles based on dexamethasone polyethylenimine nanoliposomes: Preparation and evaluation of transfection efficiency.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 May 1;165:252-261. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.02.043. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 29494955
-
Quantification of cellular and nuclear uptake rates of polymeric gene delivery nanoparticles and DNA plasmids via flow cytometry.Acta Biomater. 2016 Jun;37:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.036. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27019146 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to non-viral vector-mediated gene delivery in the nervous system.Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;28(8):1843-58. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0364-7. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 21225319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coaxial Synthesis of PEI-Based Nanocarriers of Encapsulated RNA-Therapeutics to Specifically Target Muscle Cells.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 22;12(8):1012. doi: 10.3390/biom12081012. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35892322 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospray for generation of drug delivery and vaccine particles applied in vitro and in vivo.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Dec;105:110070. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110070. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31546372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of novel gene carrier using modified nano hydroxyapatite derived from equine bone for osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells.Bioact Mater. 2021 Feb 13;6(9):2742-2751. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.01.020. eCollection 2021 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2021. PMID: 33665505 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical simulations of wall contact angle effects on droplet size during step emulsification.RSC Adv. 2018 Sep 25;8(58):33042-33047. doi: 10.1039/c8ra06837b. eCollection 2018 Sep 24. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35548132 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional mesenchymal stem cell laden scaffold of icariin sustained-release for bone regeneration.Turk J Biol. 2022 Sep 2;46(5):414-425. doi: 10.55730/1300-0152.2627. eCollection 2022. Turk J Biol. 2022. PMID: 37529003 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

