Piezoelectric effect stimulates the rearrangement of chondrogenic cells and alters ciliary orientation via atypical PKCζ
- PMID: 35540436
- PMCID: PMC9079777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101265
Piezoelectric effect stimulates the rearrangement of chondrogenic cells and alters ciliary orientation via atypical PKCζ
Abstract
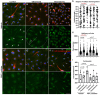
Therapeutic ultrasound was administered to patients suffering from bone fracture with FDA approval. Bone and cartilage are piezoelectric materials. To investigate the effects of piezoelectricity on the cells of chondrogenic lineage, we applied ultrasound stimulation on an AT-cut quartz coverslip to generate electric field fluctuations. The bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSC) and primary chondrocytes were cultured on either glass or quartz coverslips for ultrasound stimulation. The cells were immunofluorescent-labeled for the assessment of cell arrangement and ciliary orientation. Ultrasound and piezoelectricity both stimulate cell migration and disrupt ciliary orientation induced by directional migration. In particular, piezoelectric effects on cell rearrangement can be abolished by the inhibitor specifically targeting atypical Protein kinase C zeta (PKCζ). Our findings shed light on the possibility of cellular modulation by using piezoelectric manipulation.
Keywords: Cell rearrangement; Chondrogenic cells; Ciliary orientation; PKCζ; Piezoelectric stimulation.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Chen C., Zhang T., Liu F., Qu J., Chen Y., Fan S., Chen H., Sun L., Zhao C., Hu J., Lu H. Effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound after autologous adipose-derived stromal cell transplantation for bone-tendon healing in a rabbit model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019;47:942–953. doi: 10.1177/0363546518820324. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

