The inhibiting role of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate on piperine crystallization to enhance its dissolution from its amorphous solid dispersion and permeability
- PMID: 35540632
- PMCID: PMC9076092
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra08283b
The inhibiting role of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate on piperine crystallization to enhance its dissolution from its amorphous solid dispersion and permeability
Abstract
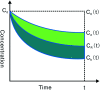
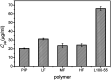
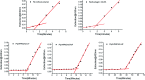
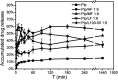
The purpose of this study was to demonstrate that inhibiting crystallization by HPMCAS played a key role in enhancing dissolution and absorption of piperine (Pip) from its amorphous solid dispersion (ASD). Nucleation induction time and supersaturation tests were used to evaluate the ability of the polymers to inhibit crystallization of Pip. The prepared solid dispersions were characterized by DSC and FTIR. The dissolution rate of Pip from its ASDs was assayed by a dissolution test. Pip permeability was investigated by single-pass intestinal perfusion studies. The order of the ability of polymers to inhibit Pip crystallization was HF > MF > LF > L100-55. The best inhibition effect of HF can be attributed to its hydrophobicity and steric hindrance. Pip is amorphous in polymer matrices when the ratio of Pip/HPMCAS is lower than 1 : 1 and Pip/L100-55 is lower than 3 : 1. IR spectra show that there are hydrogen bonds between the amide groups of Pip and the carboxyl groups of polymer. The order of the ability of polymers to enhance Pip dissolution is HF > MF > LF > L100-55, which coincided with the ability of polymers to inhibit Pip crystallization. Increased apparent permeability via HF-induced supersaturation and decreased apparent permeability via solubilization with L100-55 are demonstrated. Nucleation induction time and supersaturation tests may be used to screen appropriate polymers for preparing ASDs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Amorphous Quercetin/ Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose Acetate Succinate Solid Dispersions Prepared by Co-Precipitation Method to Enhance Quercetin Dissolution.J Pharm Sci. 2021 Sep;110(9):3230-3237. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2021.05.004. Epub 2021 May 15. J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34004218
-
[Effect of HPMCAS/curcumin amorphous solid dispersion in enhancing dissolution and chemical stability of curcumin].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Aug;44(15):3305-3311. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190516.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31602887 Chinese.
-
Enteric Polymer-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersions Enhance Oral Absorption of the Weakly Basic Drug Nintedanib via Stabilization of Supersaturation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 30;14(9):1830. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091830. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145578 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanistic review on the dissolution phase behavior and supersaturation stabilization of amorphous solid dispersions.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021 Jan;47(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2021.1879843. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33494623 Review.
-
Role of Permeability on the Biopredictive Dissolution of Amorphous Solid Dispersions.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Sep 30;22(7):243. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02125-4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 34595565 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Properties of Pterostilbene (Resveratrol Derivative) in Amorphous Solid Dispersions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 28;25(5):2774. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052774. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474022 Free PMC article.
-
Enteric coating of tablets containing an amorphous solid dispersion of an enteric polymer and a weakly basic drug: A strategy to enhance in vitro release.Int J Pharm. 2023 Jul 25;642:123139. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123139. Epub 2023 Jun 11. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37311499 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Delayed Release Oral Formulation Comprising Esomeprazole Spray Dried Dispersion Utilizing Design of Experiment As An Optimization Strategy.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Sep 12;24(7):186. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02642-4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 37700215
-
Hot-melt extruded hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate based amorphous solid dispersions: Impact of polymeric combinations on supersaturation kinetics and dissolution performance.Int J Pharm. 2022 Mar 5;615:121471. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121471. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35041915 Free PMC article.
-
Supersaturation Behavior: Investigation of Polymers Impact on Nucleation Kinetic Profile for Rationalizing the Polymeric Precipitation Inhibitors.Curr Drug Deliv. 2024;21(10):1422-1432. doi: 10.2174/0115672018261505231018100329. Curr Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 37907490
References
-
- Chau L. N. V. Chulhun P. Lee B. J. Current trends and future perspectives of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013;85:799–813. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

