Analysis of volatile compounds in fresh sturgeon with different preservation methods using electronic nose and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry
- PMID: 35540663
- PMCID: PMC9075984
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06287d
Analysis of volatile compounds in fresh sturgeon with different preservation methods using electronic nose and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry
Abstract
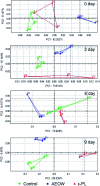
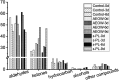
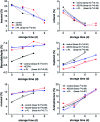
Contamination of microorganisms causes a rapid deterioration in the quality of fresh sturgeon meat, which results in the shortening of the shelf-life and increase in the health risk. In this paper, two preservation treatments based on microbial control were considered. During the chilling storage (0-6 days) period, the sensory analysis and the volatile compound (VOC) evaluation were performed by electronic nose and SPME-GC/MS. Results showed that washing with acidic oxidized electrolyzed water and the addition of ε-PL influences the sensitive VOCs of the fresh sturgeon by inhibiting the spoilage of microbes or introducing the chemical agents like free chlorine and reactive oxygen species. Furthermore, GC/MS analysis detected more than 40 kinds of VOCs, mainly aldehydes and ketones, in the fresh sturgeon during the chilling storage period. The relative content of heptanal, nonanal, and acetophenone increased linearly with the storage time in all the groups, where R 2 of all the groups was larger than 0.9. However, the content of hexanal and octanal decreased simultaneously. This indicated that the present work discovered the potential biomarkers acting as indicators for rapidly evaluating the quality of sturgeon products.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of the Specific Spoilage Organism in Farmed Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) Fillets and Its Associated Quality and Flavour Change during Ice Storage.Foods. 2021 Aug 28;10(9):2021. doi: 10.3390/foods10092021. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34574132 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Effects of Biochemical Drivers on the Bacterial Communities and Volatile Profiles in Refrigerated Sturgeon Filets at 4°C.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 30;13:849236. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.849236. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35432233 Free PMC article.
-
Change of volatile compounds in fresh fish meat during ice storage.J Food Sci. 2011 Nov-Dec;76(9):C1319-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02388.x. Epub 2011 Oct 4. J Food Sci. 2011. PMID: 22416694
-
Bacterial populations and the volatilome associated to meat spoilage.Food Microbiol. 2015 Feb;45(Pt A):83-102. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25481065 Review.
-
Applications of Electronic Nose, Electronic Eye and Electronic Tongue in Quality, Safety and Shelf Life of Meat and Meat Products: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;23(2):672. doi: 10.3390/s23020672. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Flavor Profiles of Highland Barley Fermented with Different Mushroom Mycelium.Foods. 2022 Dec 7;11(24):3949. doi: 10.3390/foods11243949. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36553692 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in Antarctic krill paste with different processing methods based on GC-IMS.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Sep 2;12(10):8353-8363. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4425. eCollection 2024 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39479678 Free PMC article.
-
Wild-Grown Romanian Eupatorium cannabinum: Advancing Phyto-Nanocarriers via Maltodextrin Micro-Spray Encapsulation-Metabolite Profiling, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxicity Insights.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;17(4):482. doi: 10.3390/polym17040482. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006144 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

