Associations between Serum Interleukins (IL-1 β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10) and Disease Severity of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35540724
- PMCID: PMC9079324
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2755246
Associations between Serum Interleukins (IL-1 β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10) and Disease Severity of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: To investigate the association between interleukins (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10) and the disease severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
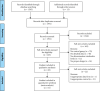
Materials and methods: We systematically searched records investigating the role of interleukins (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10) in COVID-19 patients in Web of Science, Pubmed, and Embase through December 2020. Data were extracted and pooled, and the weighted mean difference (WMD) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated. The funnel plot and the nonparametric trim and fill method were used to visualize and adjust the publication bias.
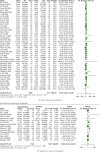
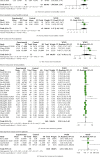
Results: In total, 61 studies enrolled 14,136 subjects (14,041 patients and 95 healthy subjects) were enrolled in this meta-analysis. Our results showed that serum IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 levels were elevated in COVID-19 patients compared to healthy controls, and IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 levels were increased in severe COVID-19 cases compared to nonsevere patients. Additionally, the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 were elevated in nonsurvivor patients compared to survivors. For patients in the intensive care unit (ICU), IL-6 and IL-8 levels were increased than that in non-ICU patients.
Conclusions: Elevated levels of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 were associated with the disease severity of COVID-19, and elevated levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 were related to the prognosis of COVID-19 patients, which could be used to evaluate COVID-19 patients' disease severity and prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Yuanmin Chang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no potential conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures





Similar articles
-
COVID-19 and coagulation dysfunction in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2021 Feb;93(2):934-944. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26346. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32706426 Free PMC article.
-
Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Jun 25;58(7):1021-1028. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0369. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32286245 Review.
-
Association of inflammatory markers with the severity of COVID-19: A meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;96:467-474. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.055. Epub 2020 May 18. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32425643 Free PMC article.
-
A score combining early detection of cytokines accurately predicts COVID-19 severity and intensive care unit transfer.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;101:342-345. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33039609 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of serum interleukin-1β levels as a potential indicator for malarial infection and severe malaria: a meta-analysis.Malar J. 2022 Oct 29;21(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12936-022-04325-0. Malar J. 2022. PMID: 36309676 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cytokine levels associated with favorable clinical outcome in the CAPSID randomized trial of convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 6;13:1008438. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1008438. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275695 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of Baculovirus-Expressed SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein in Mice as a Universal Vaccine Candidate.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;12(9):977. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12090977. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39340009 Free PMC article.
-
The shed P2X7 receptor is an index of adverse clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients.Front Immunol. 2023 May 5;14:1182454. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1182454. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37215142 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of plasma soluble receptors of TNF and IL-1 in patients with COVID-19 differs from that observed in sepsis.J Infect. 2024 Dec;89(6):106300. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106300. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Infect. 2024. PMID: 39357572 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Insight into Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Benefits of Chinese Herbal Medicines.Medicines (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;11(7):14. doi: 10.3390/medicines11070014. Medicines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39051370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

