Transcriptomic analysis of thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus in multiple inhibitors tolerance
- PMID: 35540752
- PMCID: PMC9079866
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00335a
Transcriptomic analysis of thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus in multiple inhibitors tolerance
Abstract
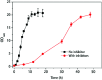
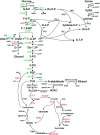
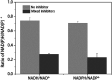
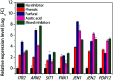
During pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass, toxic compounds were released and inhibited the growth and fermentation of microorganisms. Here the global transcriptional response of K. marxianus to multiple inhibitors including acetic acid, phenols, furfural and HMF, at 42 °C, was studied, via RNA-seq technology. Genes involved in the glycolysis pathway, fatty acid metabolism, ergosterol metabolism and vitamin B6 and B1 metabolic process were enriched in the down-regulated gene set, while genes involved in TCA cycle, respiratory chain, ROS detoxification and transporter coding genes were enriched in the up-regulated gene set in response to the multiple inhibitors stress. Further real time-PCR results with three single inhibitor stress conditions showed that different transporters responded quite differently to different inhibitor stress. Coenzyme assay results showed that the level of NAD+ was increased and both NADH/NAD+ and NADPH/NADP+ ratio decreased. Furthermore, genes involved with transcription factors related to carbohydrate metabolism, sulfur amino acids metabolism, lipid metabolism or those directly involved in the transcriptional process were significantly regulated. Though belonging to different GO categories or KEGG pathway, many differentially expressed genes were enriched in maintaining the redox balance, NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H homeostasis or NAD+ synthesis, energy production, and iron transportation or metabolism. These results suggest that engineering these aspects represents a possible strategy to develop more robust strains for industrial fermentation from cellulosic biomass.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

