Synthesis of polyurethanes with pendant azide groups attached on the soft segments and the surface modification with mPEG by click chemistry for antifouling applications
- PMID: 35540978
- PMCID: PMC9080695
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02912a
Synthesis of polyurethanes with pendant azide groups attached on the soft segments and the surface modification with mPEG by click chemistry for antifouling applications
Abstract
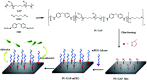
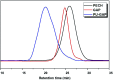
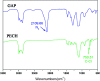
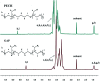
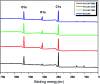
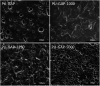
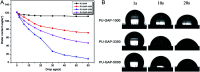
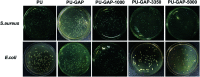
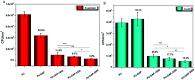
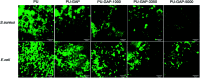
Polyurethane with pendant azide groups on the soft segment (PU-GAP) was prepared in this study to further increase the content of reactive azide groups and improve their surfaces enrichment for further functionalization. Polymer diols with pendant azide groups (GAP) were prepared by transforming the pendant chlorine groups at polyepichlorohydrin (PECH) into azide groups with sodium azide. The prepared PECH, GAP and PU-GAP was characterized by GPC, 1H NMR and FTIR. Propargylic mPEG (mPEG-alkyne) was used as model surface modification reagents which was grafted on the prepared azido containing polyurethane films via click chemistry. The surface morphology, chemical composition and wettabilities were studied by SEM, XPS and water contact angle (WCA) analysis, respectively. SEM results demonstrated different surface topologies between mPEG modified PU surface and original PU surface. XPS and WCA analysis proved the successful grafting of mPEG on the pendant azide groups of PUs. The mPEG modified PU surfaces demonstrated good antifouling activities against model bacteria and mPEG with larger molecular weights modified surfaces showed better resistance efficiency to attachment of bacteria. Therefore, the surface reactive polyurethane we prepared can be a universal platform for further functionalization according actual applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
Synthesis of low surface-energy polyepichlorohydrin triazoles thin film.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Mar 15;539:481-489. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.12.102. Epub 2018 Dec 29. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 30611043
-
A dynamic duo: pairing click chemistry and postpolymerization modification to design complex surfaces.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Oct 21;47(10):2999-3008. doi: 10.1021/ar500191m. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25127014
-
Surface modification of polyethersulfone membranes by blending triblock copolymers of methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol)-polyurethane-methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol).Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011 Nov 1;88(1):315-24. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011. PMID: 21802912
-
Surface functionalization of polyurethanes: A critical review.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Mar;325:103100. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103100. Epub 2024 Feb 4. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 38330882 Review.
Cited by
-
A Facile Strategy for the High Yielding, Quantitative Conversion of Polyglycol End-Groups to Amines.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;13(9):1403. doi: 10.3390/polym13091403. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33926044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lv X. Wang X. Guo L. et al., Preparation of PU modified PVDF antifouling membrane and its hydrophilic performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2016;520:933–940. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2016.08.018. - DOI
-
- Rana S. Lee S. Y. Cho J. W. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible poly(ethylene glycol)-functionalized polyurethane using click chemistry. Polym. Bull. 2009;64(4):401–411. doi: 10.1007/s00289-009-0175-3. - DOI
-
- Yuan S. Luan S. Yan S. et al., Facile Fabrication of Lubricant-Infused Wrinkling Surface for Preventing Thrombus Formation and Infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015;7(34):19466–19473. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

