Enhanced osteogenic activity of Ti alloy implants by modulating strontium configuration in their surface oxide layers
- PMID: 35541194
- PMCID: PMC9077531
- DOI: 10.1039/c7ra10807a
Enhanced osteogenic activity of Ti alloy implants by modulating strontium configuration in their surface oxide layers
Abstract
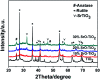
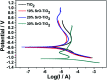
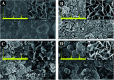
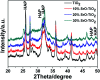
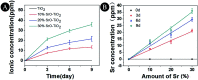
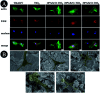
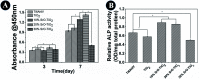
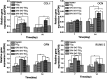
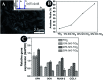
To guarantee the long-term stability of an orthopaedic implant, non-degradable surface coatings with the ability to selectively release bioactive drugs or ions are especially desirable. In this study, SrO-TiO2 composite coatings were deposited on the surface of Ti alloys, whose release behavior of bioactive Sr ions was modulated by the Sr configurations, either interstitial atoms in solid solution (Ti y Sr2-2y O2) or strontium titanate (SrTiO3). A perfect linear relationship between the amount of the released Sr ions and the Sr content in the coating was observed. Among the SrO-doped TiO2 coatings, the 20% SrO-TiO2 coating where Sr existed in both forms of Ti y Sr2-2y O2 and SrTiO3 not only promoted proliferation of bone cells but also enhanced their osteogenic differentiation, which was proved to be related to its Sr release behavior. However, overdosing with 30% SrO only resulted in one single Sr configuration (SrTiO3) and an inferior osteogenic function. This study suggests that Sr configurations of both interstitial atoms of the solid solution and SrTiO3 can realize the selective release of Sr, but they possibly have different effects on the biological functions and other properties including corrosion resistance.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrodeposition of Sr-substituted hydroxyapatite on low modulus beta-type Ti-45Nb and effect on in vitro Sr release and cell response.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Mar;108:110425. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110425. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 31923935
-
Evaluation of osteogenic and antibacterial properties of strontium/silver-containing porous TiO2 coatings prepared by micro-arc oxidation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021 Apr;109(4):505-516. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34719. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021. PMID: 32865337
-
Fabrication of TiO2-strontium loaded CaSiO3/biopolymer coatings with enhanced biocompatibility and corrosion resistance by controlled release of minerals for improved orthopedic applications.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016 Jul;60:476-491. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.02.021. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016. PMID: 27018944
-
Phase stability and biological property evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for orthopedic and dental applications.Acta Biomater. 2015 Apr;17:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.01.022. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25638672 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of corrosion resistance between beta titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloys: A systematic review.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Dec;62:126618. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126618. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32663743
Cited by
-
Enhanced biological performance of Sr2+-doped nanorods on titanium implants by surface thermal-chemical treatment.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2025 Jun 23;36(1):54. doi: 10.1007/s10856-025-06898-z. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2025. PMID: 40549257 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the coexistence of albumin and H2O2 on the corrosion of biomedical cobalt alloys in physiological saline.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 15;9(57):32954-32965. doi: 10.1039/c9ra05699h. eCollection 2019 Oct 15. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35529113 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

