Catalytic oxidation of CO over mesoporous copper-doped ceria catalysts via a facile CTAB-assisted synthesis
- PMID: 35541330
- PMCID: PMC9079958
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02327a
Catalytic oxidation of CO over mesoporous copper-doped ceria catalysts via a facile CTAB-assisted synthesis
Abstract
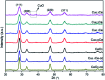
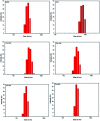
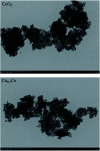
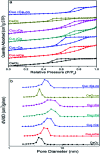
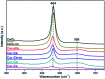
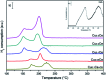
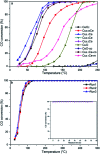
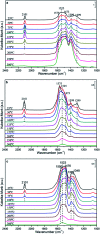
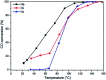
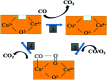
Nanosized copper-doped ceria CuCe catalysts with a large surface area and well-developed mesoporosity were synthesized by a surfactant-assisted co-precipitation method. The prepared catalysts with different Cu doping concentrations were characterized by XRD, DLS analysis, TEM, BET, Raman, H2-TPR and in situ DRIFTS techniques. The influence of Cu content on their catalytic performance for CO oxidation was also studied. The XRD results indicate that at a lower content, the Cu partially incorporates into the CeO2 lattice to form a CuCe solid solution, whereas a higher Cu doping causes the formation of bulk CuO. Copper doping favors an increase in the surface area of the CuCe catalysts and the formation of oxygen vacancies, thereby improving the redox properties. The CuCe samples exhibit higher catalytic performance compared to bare CeO2 and CuO catalysts. This is ascribed to the synergistic interaction between copper oxide and ceria. In particular, the Cu0.1Ce catalyst shows the highest catalytic performance (T 50 = 59 °C), as well as excellent stability. The in situ DRIFTS results show that CO adsorbed on surface Cu+ (Cu+-CO species) can easily react with the active oxygen, while stronger adsorption of carbonate-like species causes catalyst deactivation during the reaction.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Catalytic oxidation of soot on mesoporous ceria-based mixed oxides with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB)-assisted synthesis.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Dec 15;508:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.07.114. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28810164
-
Double redox process to synthesize CuO-CeO2 catalysts with strong Cu-Ce interaction for efficient toluene oxidation.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Feb 15;404(Pt A):124088. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124088. Epub 2020 Oct 2. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33053474
-
Enhanced Catalytic Performance of (CuO)x /Ce0.9 Cu0.1 O2 Nanospheres: Combined Contribution of the Synergistic Effect and Surface Defects.Chempluschem. 2015 May;80(5):886-894. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201402328. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Chempluschem. 2015. PMID: 31973336
-
An Insight into Geometries and Catalytic Applications of CeO2 from a DFT Outlook.Molecules. 2021 Oct 27;26(21):6485. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216485. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ceria in the improvement of NO removal of lanthanum-based perovskite-type catalysts.RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 27;8(21):11778-11784. doi: 10.1039/c8ra00456k. eCollection 2018 Mar 21. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35542810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low temperature CO oxidation by doped cerium oxide electrospun fibers.Nano Converg. 2020 Jun 29;7(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40580-020-00234-7. Nano Converg. 2020. PMID: 32602081 Free PMC article.
-
Combustion Synthesis of Non-Precious CuO-CeO₂ Nanocrystalline Catalysts with Enhanced Catalytic Activity for Methane Oxidation.Materials (Basel). 2019 Mar 15;12(6):878. doi: 10.3390/ma12060878. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30875991 Free PMC article.
-
Sorption Profile of Low Specific Activity 99Mo on Nanoceria-Based Sorbents for the Development of 99mTc Generators: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 May 7;12(9):1587. doi: 10.3390/nano12091587. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35564296 Free PMC article.
-
PROMETHEUS: A Copper-Based Polymetallic Catalyst for Automotive Applications. Part I: Synthesis and Characterization.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jan 29;14(3):622. doi: 10.3390/ma14030622. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572954 Free PMC article.
-
An eco-friendly route for template-free synthesis of high specific surface area mesoporous CeO2 powders and their adsorption for acid orange 7.RSC Adv. 2019 Jul 18;9(39):22366-22375. doi: 10.1039/c9ra02294e. eCollection 2019 Jul 17. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35519489 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

