Retracted Article: MicroRNA-1271 modulates hepatitis B virus replication, cell proliferation and apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SIRT1
- PMID: 35541395
- PMCID: PMC9076187
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra08248d
Retracted Article: MicroRNA-1271 modulates hepatitis B virus replication, cell proliferation and apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SIRT1
Retraction in
-
Retraction: MicroRNA-1271 modulates hepatitis B virus replication, cell proliferation and apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SIRT1.RSC Adv. 2021 Feb 1;11(10):5698. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90060a. eCollection 2021 Jan 28. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35427030 Free PMC article.
Abstract
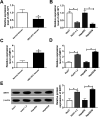
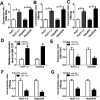
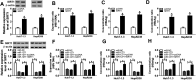
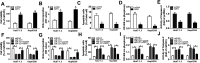
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Certain studies have revealed that microRNAs play crucial roles in HBV-related HCC. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of microRNA-1271 (miR-1271) on HBV replication, cell proliferation and apoptosis in HBV-related HCC. The expression of HBV DNA and miR-1271 was detected by quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The mRNA and protein levels of SIRT1 were detected by qRT-PCR and western blot analysis, respectively. HBV replication was assessed by the expression of HBV DNA and the levels of HBsAg and HBeAg. Cell proliferation was assessed by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-bromo-2-deoxyuidine (BrdU) assay, and apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the activity of caspase-3. The relationship between miR-1271 and SIRT1 was predicated by online software and confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and pull-down assay. We first found that the expression of miR-1271 was downregulated and SIRT1 was upregulated in both HBV-related HCC tissues and cells. Overexpression of miR-1271 inhibited HBV replication and cell proliferation whilst promoting apoptosis in HBV-related HCC cells. Subsequently, SIRT1 was identified as a target of miR-1271. Moreover, overexpression of SIRT1 reversed the effects of miR-1271 overexpression on HBV replication, cell proliferation and apoptosis in HBV-related HCC cells. In conclusion, our study demonstrated that miR-1271 inhibited HBV replication and proliferation and promoted apoptosis of HBV-related HCC cells via targeting SIRT1, which might contribute to the diagnosis and therapy of HBV-related HCC.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

