Sheath-less high throughput inertial separation of small microparticles in spiral microchannels with trapezoidal cross-section
- PMID: 35541623
- PMCID: PMC9076541
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra05916d
Sheath-less high throughput inertial separation of small microparticles in spiral microchannels with trapezoidal cross-section
Abstract
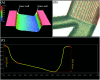
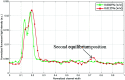
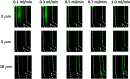
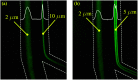
Various mechanisms of different designs have emerged for the purpose of microparticle separation and cell sorting. The main goals behind such designs are to create high throughput and high purity sample isolation. In this study, high efficiency, high throughput and precise separation of microparticles under inertial lift and drag forces induced by trapezoidal curvilinear channels are reported. This work is the first to focus and recover 2 from 5 μm and 2 from 10 μm particles in spiral channels in a sheath-less flow device, which reduces the overall complexity of the system and allows for higher throughput. The new microfluidic chip design is fabricated in glass using femtosecond laser ablation. In addition, mathematical force calculations were conducted during the design phase of the microfluidic channels and compared with experiments. The results show a close prediction of the equilibrium position of the tested microparticles.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Moloudi R. Oh S. Yang C. Ebrahimi Warkiani M. Naing M. W. Microfluid. Nanofluidics. 2018;22:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10404-017-2014-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

