Promotion of autophagosome-lysosome fusion via salvianolic acid A-mediated SIRT1 up-regulation ameliorates alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 35541657
- PMCID: PMC9080827
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00798e
Promotion of autophagosome-lysosome fusion via salvianolic acid A-mediated SIRT1 up-regulation ameliorates alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
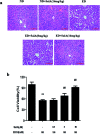
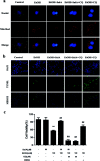
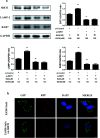
Salvianolic acid A (SalA) is a water-soluble phenolic carboxylic acid extracted from Salvia miltiorrhiza that has extensive pharmacological activities and plays an essential role in liver disease treatment. However, the mechanism of SalA in treating alcoholic liver disease (ALD) remains unclear. Here, we studied the protective effects of SalA on chronic ethanol-induced liver injury involving Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-mediated autophagy activation. The results showed that SalA pretreatment reduced the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol (TC) in vivo and enhanced hepatic cell viability while mitigating apoptosis and hepatic steatosis in vitro. Furthermore, SalA protected against chronic ethanol-induced liver injury by restoring autophagosome-lysosome fusion, as indicated by the increased expression levels of LC3-II, cathepsin B, lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP-2), and RAB7 and the decreased expression of SQSTM1. More importantly, pretreatment with SalA significantly up-regulated the expression of SIRT1, an NAD+-dependent deacetylase. These increased levels of SIRT1 stimulated autophagy under conditions of chronic ethanol exposure. Interestingly, SIRT1 siRNA abrogated SalA-induced autophagosome-lysosome fusion. This finding indicates that the protective effects of SalA are associated with SIRT1 activation. Collectively, our study demonstrates that SalA pretreatment protects against chronic ethanol-induced liver injury via the SIRT1-mediated restoration of autophagosome-lysosome fusion.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

