Frontier challenges in doping quantum dots: synthesis and characterization
- PMID: 35541736
- PMCID: PMC9081084
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra03530j
Frontier challenges in doping quantum dots: synthesis and characterization
Abstract
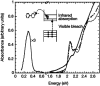
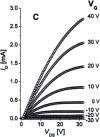
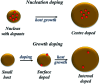
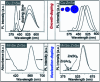
Impurity doping in semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) has numerous prospects in implementing and altering their properties and technologies. Herein, we review the state-of-the-art doping techniques arising from colloidal synthesis methods. We first discuss the advantages and challenges involved in doping; we then discuss various doping techniques, including clustering of dopants as well as expulsion out of the lattice due to self-purification. Some of these techniques have been shown to open up a new generation of robust doped semiconductor quantum dots with cluster-free doping which will be suitable for various spin-based solid-state device technologies and overcome the longstanding challenges of controlled impurity doping. Further, we discuss inhibitors such as defects, clustering and interfaces, followed by current open questions. These include pathways to obtain uniform doping in the required radial position with unprecedented control over the dopant concentration and the size of the QDs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


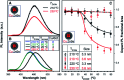
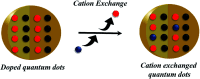
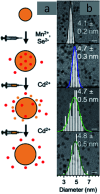
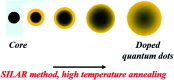


References
-
- Norris D. J. Yao N. Charnock F. T. Kennedy T. A. Nano Lett. 2001;1:3–7. doi: 10.1021/nl005503h. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

