GPI0363 inhibits the interaction of RNA polymerase with DNA in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35541796
- PMCID: PMC9075815
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06844a
GPI0363 inhibits the interaction of RNA polymerase with DNA in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
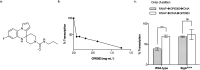
We previously reported a therapeutically effective spiro-heterocyclic compound, GPI0363, that inhibits the transcription of Staphylococcus aureus via the primary sigma factor of RNA polymerase, SigA. Here, we demonstrated that GPI0363 shares no cross-resistance with the clinically used RNA polymerase inhibitors rifampicin and fidaxomicin. Furthermore, we found that GPI0363 bound to SigA of both GPI0363-susceptible and resistant strains, and inhibited the interaction of the RNA polymerase holoenzyme with DNA. In addition, the gene expression patterns following GPI0363 treatment were different from those following rifampicin treatment. These findings suggest that GPI0363 has a unique mechanism of action and can serve as a promising lead molecule to develop staphylococcal RNA polymerase inhibitors.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel Spiro-Heterocyclic Compound Identified by the Silkworm Infection Model Inhibits Transcription in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 25;8:712. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00712. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28487682 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of transcription in Staphylococcus aureus by a primary sigma factor-binding polypeptide from phage G1.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(12):3763-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.00241-09. Epub 2009 Apr 17. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19376864 Free PMC article.
-
A new class of small molecule RNA polymerase inhibitors with activity against rifampicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Sep 1;14(17):5812-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.05.035. Epub 2006 Jun 8. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16759869
-
Genetic profile mutation rpoB in clinical isolate of rifampicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 25;32(4):773-776. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2020-0444. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34214301
-
Targeting RNA polymerase primary σ70 as a therapeutic strategy against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by antisense peptide nucleic acid.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029886. Epub 2012 Jan 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253815 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Target identification of usnic acid in bacterial and human cells.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 May 7;5(7):617-621. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00040d. eCollection 2024 Jul 3. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38966671 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Amino Acid Substitution in HepT Toward Menaquinone Isoprenoid Chain Length Definition and Lysocin E Sensitivity in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 26;11:2076. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02076. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32983054 Free PMC article.
-
Silkworm model of bacterial infection facilitates the identification of lysocin E, a potent, ultra-rapid bactericidal antibiotic.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024 Aug;77(8):477-485. doi: 10.1038/s41429-024-00739-x. Epub 2024 May 21. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 38773231 Review.
-
Unlocking Opportunities for Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium ulcerans.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Feb 9;10(2):251-269. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00371. Epub 2024 Jan 31. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38295025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indolin-2-one Nitroimidazole Antibiotics Exhibit an Unexpected Dual Mode of Action.ACS Chem Biol. 2022 Nov 18;17(11):3077-3085. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00462. Epub 2022 Oct 19. ACS Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 36259427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McClure W. R. Cech C. L. J. Biol. Chem. 1978;253:8949–8956. - PubMed
-
- Lin W. Das K. Degen D. Mazumder A. Duchi D. Wang D. Ebright Y. W. Ebright R. Y. Sineva E. Gigliotti M. Srivastava A. Mandal S. Jiang Y. Liu Y. Yin R. Zhang Z. Eng E. T. Thomas D. Donadio S. Zhang H. Zhang C. Kapanidis A. N. Ebright R. H. Mol. Cell. 2018;70:60–71. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Srivastava A. Talaue M. Liu S. Degen D. Ebright R. Y. Sineva E. Chakraborty A. Druzhinin S. Y. Chatterjee S. Mukhopadhyay J. Ebright Y. W. Zozula A. Shen J. Sengupta S. Niedfeldt R. R. Xin C. Kaneko T. Irschik H. Jansen R. Donadio S. Connell N. Ebright R. H. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011;14:532–543. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.07.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

