MiR-29c inhibits HCV replication via activation of type I IFN response by targeting STAT3 in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells
- PMID: 35542013
- PMCID: PMC9078521
- DOI: 10.1039/c7ra12815k
MiR-29c inhibits HCV replication via activation of type I IFN response by targeting STAT3 in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells
Abstract
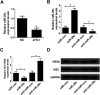
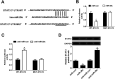
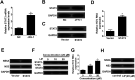
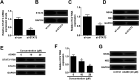
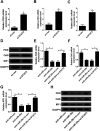
Background: MiR-29c, a member of the miR-29 family, has been recognized to play an important role in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of miR-29c involved in HCV replication is not fully understood. Methods: RT-qPCR assay was used to detect the expression pattern of miR-29c and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) mRNA in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells. HCV replication was evaluated by the expression of HCV RNA, non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) and non-structural protein 3 (NS3). Dual-Luciferase Reporter assay was applied to search for the candidate target mRNAs of miR-29c. Western blot assay was performed to detect the protein level of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase R (PKR), (2'-5')-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) and interferon regulatory transcription factor 1 (IRF1). Results: miR-29c expression was down-regulated, and STAT3 mRNA and protein expressions were up-regulated in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells. MiR-29c overexpression or STAT3 knockdown repressed HCV replication, while miR-29c depletion or STAT3 upregulation promoted HCV replication. Additionally, STAT3 was a direct target of miR-29c, and miR-29c suppressed STAT3 protein expression in Huh7 cells. Moreover, STAT3 overexpression reversed miR-29c-mediated suppression on HCV replication. Furthermore, the anti-miR-29c-mediated inhibitory effect on type I IFN response was abated following STAT3 knockdown. Conclusions: miR-29c might repress HCV infection via promoting type I IFN response by targeting STAT3 in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells, offering a promising avenue for HCV treatment.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Wang S. H., Yeh S. H. and Chen P. J., Hepatitis C Virus II, 2016, pp. 109–136
-
- Wakita T. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009;510:305–327. - PubMed
-
- Welzel T. Petersen J. Herzer K. Ferenci P. Gschwantler M. Cornberg M. Ingiliz P. Berg T. Spengler U. Weiland O. J. Hepatol. 2016;64:S781–S782.
-
- Horsleysilva J. L. Vargas H. E. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;48:22–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

