Automated 96-well format high throughput colony formation assay for siRNA library screen
- PMID: 35542177
- PMCID: PMC9079112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101355
Automated 96-well format high throughput colony formation assay for siRNA library screen
Abstract
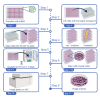
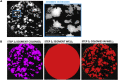
The colony formation assay is the gold-standard technique to assess cell viability after treatment with cytotoxic reagents, ionizing radiation, and cytotoxic combinatorial treatments. This protocol describes a high-throughput automated and high-content imaging approach to screen siRNA molecular libraries in HeLa cervical cancer cells in 96-well format. We detail reverse transfection of cells with siRNAs, followed by ionizing radiation, fixing, and staining of the plates for automated colony counting. This protocol can be used across a broad range of cell types. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Tiwana et al. (2015).
Keywords: Cancer; Cell Biology; Cell culture; Cell-based Assays; High Throughput Screening; Molecular Biology; Single Cell.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lundholt B.K., Scudder K.M., Pagliaro L. A simple technique for reducing edge effect in cell-based assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 2003;8:566–570. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J.-H., Chung T.D.Y., Oldenburg K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999;4:67–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

