Probing hemoglobin glyco-products by fluorescence spectroscopy
- PMID: 35542272
- PMCID: PMC9075759
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra05243g
Probing hemoglobin glyco-products by fluorescence spectroscopy
Abstract
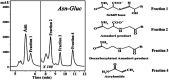
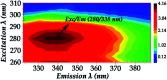
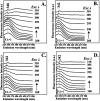
Maillard reaction products (MRPs) participate in reactions of carbohydrate intermediates with proteins, resulting in the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). Dietary Maillard reaction products are recognized as potential chemical modifiers of human proteins. We have investigated the reaction of isolated MRPs from an asparagine-glucose model system with hemoglobin (Hb) to elucidate the binding effect of the MRPs in hemoglobin by fluorescence spectrophotometry. The tryptophan-specific fluorescence obtained for glycated hemoglobin exhibited a Stokes effect since the wavelength of the emission peak was shifted to a higher wavelength than that of native Hb. The formation of new fluorescence emission features indicates the formation of modified hemoglobin species. Fluorescence spectroscopic studies provide evidence that the conformational changes in the β-Trp 37 moiety induce motion of the distal His 64 (E7) in the heme binding pocket. This results in the formation of inactive hemichrome forms of hemoglobin which are related to blood disorders.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Friedman M. Food browning and its prevention: an overview. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996;44:631–653. doi: 10.1021/jf950394r. - DOI
-
- Buera M. D. P. Chirife J. Resnik S. L. Wetzler G. Nonenzymatic browning in liquid model systems of high water activity: kinetics of color changes due to Maillard's reaction between different single sugars and glycine and comparison with caramelization browning. J. Food Sci. 1987;52:1063–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1987.tb14276.x. - DOI
-
- Koschinsky T. He C. J. Mitsuhashi T. Bucala R. Liu C. Buenting C. Heitmann K. Vlassara H. Orally absorbed reactive glycation products (glycotoxins): An environmental risk factor in diabetic nephropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1997;94:6474–6479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6474. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

