Curcumin improves the function of umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting H2O2‑induced pyroptosis
- PMID: 35543146
- PMCID: PMC9133960
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12730
Curcumin improves the function of umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting H2O2‑induced pyroptosis
Abstract
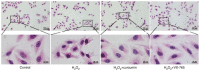
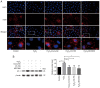
Endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction is one of the initiating factors of atherosclerosis. EC dysfunction is primarily caused by oxidative damage and inflammation. As a classic non‑specific antioxidant and anti‑inflammatory drug, curcumin has been widely used in studies of lipid metabolism disorders. However, whether curcumin is able to alleviate H2O2‑induced EC damage and its related mechanisms has remained to be elucidated. The present study confirmed the protective effects of curcumin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). A HUVEC injury model was established using H2O2 and the optimal concentrations and time of curcumin to achieve therapeutic effects were explored. Curcumin was observed to inhibit H2O2‑induced pyroptosis by inhibiting the activation of NOD‑, LRR‑ and pyrin domain‑containing protein 3. In addition, curcumin improved HUVEC function by restoring αvβ3 and reducing endothelin‑1 expression. In conclusion, the results of the present study revealed the mechanism through which curcumin inhibits pyroptosis and indicated that curcumin may have a potential utility in treating diseases of EC dysfunction.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; curcumin; endothelial cell; hydrogen peroxide; pyroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Curcumin Attenuates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Premature Senescence via the Activation of SIRT1 in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(8):1134-41. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00012. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 26235577
-
Oxymatrine attenuates oxidized low‑density lipoprotein‑induced HUVEC injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome‑mediated pyroptosis via the activation of the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Oct;48(4):187. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5020. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34368883 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 reduces H2O2‑induced HUVEC dysfunction by stimulating the sirtuin‑1/AMP‑activated protein kinase pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Jul;22(1):247-256. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11096. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32377712 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of hyperoside against H2O2-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jul;14(1):399-405. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5235. Epub 2016 May 10. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27176644
-
Curcumin Protects Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells against H2O2-Induced Cell Injury.Pain Res Manag. 2019 Sep 2;2019:3173149. doi: 10.1155/2019/3173149. eCollection 2019. Pain Res Manag. 2019. PMID: 31565108 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Review of the Protective Mechanism of Curcumin on Cardiovascular Disease.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jan 30;18:165-192. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S445555. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38312990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enrichment of decidual CD11c + CD8 + T cells with altered immune function in early pregnancy loss.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 21;16(1):6678. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61992-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40691460 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pyroptosis in Coronary Heart Disease.Anatol J Cardiol. 2024 Apr 25;28(7):318-28. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4001. Online ahead of print. Anatol J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38661060 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

