In vitro electrochemical measurement of serotonin release in the human jejunum mucosa using a diamond microelectrode
- PMID: 35543208
- PMCID: PMC9599047
- DOI: 10.1039/d2an00487a
In vitro electrochemical measurement of serotonin release in the human jejunum mucosa using a diamond microelectrode
Abstract
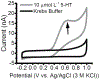
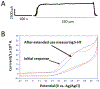
We report herein on the use of a boron-doped diamond microelectrode (DME) to record oxidation currents in vitro associated with the release of serotonin from enterochromaffin cells in the epithelium of the human intestinal mucosa. Continuous amperometric measurements were made as a function of distance (ln current vs. distance) from the tissue surface in human jejunum specimens. The results demonstrate the capabilities of the DME for the stable and reproducible detection of serotonin in the complex environment of the human tissue. Serotonin release was evoked by the shearing force of a continuously flowing Krebs buffer solution at 36 °C with the tissue pinned down in a flow bath. Reproducible currents with distance were recorded for serotonin oxidation. Increased oxidation currents were observed in the presence of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluoxetine, indicating that a significant fraction of the amperometric current recorded is attributable to serotonin oxidation. The nominal reciprocal slope, |slope-1|, of the ln current vs. distance plots increased from 270 ± 25 μm-1 in Krebs buffer (N = 3) to 471 ± 65 μm-1 during fluoxetine addition (N = 3), reflective of a reduced rate of reuptake in the presence of the SERT antagonist. The paper reports on the characterization of the diamond microelectrodes and the in vitro electrochemical measurement data.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






Similar articles
-
In vitro continuous amperometric monitoring of 5-hydroxytryptamine release from enterochromaffin cells of the guinea pig ileum.Analyst. 2007 Jan;132(1):41-7. doi: 10.1039/b611920d. Epub 2006 Nov 9. Analyst. 2007. PMID: 17180178
-
High mucosal serotonin availability in neonatal guinea pig ileum is associated with low serotonin transporter expression.Gastroenterology. 2007 Jun;132(7):2438-47. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.103. Epub 2007 Apr 13. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17570217 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous amperometric detection of co-released serotonin and melatonin from the mucosa in the ileum.Analyst. 2008 Apr;133(4):516-24. doi: 10.1039/b717034c. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Analyst. 2008. PMID: 18365122
-
Boron-doped diamond nano/microelectrodes for biosensing and in vitro measurements.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011 Jan 1;3(2):518-40. doi: 10.2741/s169. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in the applications of boron doped diamond electrodes in electroanalysis of organic compounds and biomolecules - A review.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Oct 24;1077:30-66. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.041. Epub 2019 May 22. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31307723 Review.
Cited by
-
Editors' Choice-Review-The Future of Carbon-Based Neurochemical Sensing: A Critical Perspective.ECS Sens Plus. 2023 Dec 1;2(4):043601. doi: 10.1149/2754-2726/ad15a2. Epub 2023 Dec 27. ECS Sens Plus. 2023. PMID: 38170109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Swain GM and Ramesham R, Anal. Chem, 1992, 65, 345–351.
-
- Argoitia A, Martin HB, Rozak EJ, Landau U and Angus JC, MRS Adv, 1995, 416, 349–354.
-
- Granger MC, Xu J, Strojek JW and Swain GM, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1999, 397, 145–161.
-
- Macpherson JV, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys, 2015, 17, 2935–2949. - PubMed
-
- Granger MC and Swain GM, J. Electrochem. Soc, 1999, 146, 4551–4558.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

