Seroconversion rate after primary vaccination with two doses of BNT162b2 versus mRNA-1273 in solid organ transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35544087
- PMCID: PMC9384070
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfac174
Seroconversion rate after primary vaccination with two doses of BNT162b2 versus mRNA-1273 in solid organ transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: In the general population, the seroconversion rate after primary vaccination with two doses of an anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine reaches nearly 100%, with significantly higher antibody titers after mRNA-1273 vaccination compared to BNT162b2 vaccination. Here we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the antibody response after two-dose mRNA-1273 versus BNT162b2 vaccination in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients.
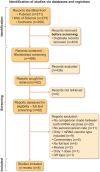
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed using PubMed, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library and original research papers were included for a meta-analysis to calculate vaccine-specific seroconversion rates for each of the mRNA vaccines. Next, the pooled relative seroconversion rate was estimated.
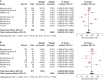
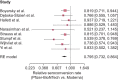
Results: Eight studies that described the development of antibodies against receptor-binding domain (RBD) and/or spike protein were eligible for meta-analysis. Two of these studies also reported antibody titers. The meta-analysis revealed lower seroconversion rates in SOT recipients vaccinated with two doses of BNT162b2 {44.3% [95% confidence interval (CI) 34.1-54.7]} as compared with patients vaccinated with two doses of mRNA-1273 [58.4% (95% CI 47.2-69.2)]. The relative seroconversion rate was 0.795 (95% CI 0.732-0.864).
Conclusions: This systematic review and meta-analysis indicates that in SOT recipients, higher seroconversion rates were observed after vaccination with mRNA-1273 compared with BNT162b2.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19; antibody response; mRNA vaccines; meta-analysis; solid organ transplant recipients.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
P.V.D. reported the University of Antwerp received research grants from GSK Biologicals, Pfizer, Sanofi, Merck, Themis, Osivax, Johnson & Johnson, Abbott, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, PATH, the Flemish government and European Union outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ (30 May 2022, date last accessed)
-
- Azzi Y, Bartash R, Scalea Jet al. COVID-19 and solid organ transplantation: a review article. Transplantation 2021; 105: 37–55 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

