Superresolution microscopy reveals actomyosin dynamics in medioapical arrays
- PMID: 35544300
- PMCID: PMC9582809
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E21-11-0537
Superresolution microscopy reveals actomyosin dynamics in medioapical arrays
Abstract
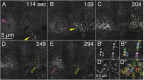
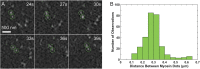
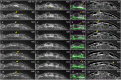
Arrays of actin filaments (F-actin) near the apical surface of epithelial cells (medioapical arrays) contribute to apical constriction and morphogenesis throughout phylogeny. Here, superresolution approaches (grazing incidence structured illumination, GI-SIM, and lattice light sheet, LLSM) microscopy resolve individual, fluorescently labeled F-actin and bipolar myosin filaments that drive amnioserosa cell shape changes during dorsal closure in Drosophila. In expanded cells, F-actin and myosin form loose, apically domed meshworks at the plasma membrane. The arrays condense as cells contract, drawing the domes into the plane of the junctional belts. As condensation continues, individual filaments are no longer uniformly apparent. As cells expand, arrays of actomyosin are again resolved-some F-actin turnover likely occurs, but a large fraction of existing filaments rearrange. In morphologically isotropic cells, actin filaments are randomly oriented and during contraction are drawn together but remain essentially randomly oriented. In anisotropic cells, largely parallel actin filaments are drawn closer to one another. Our images offer unparalleled resolution of F-actin in embryonic tissue, show that medioapical arrays are tightly apposed to the plasma membrane and are continuous with meshworks of lamellar F-actin. Medioapical arrays thereby constitute modified cell cortex. In concert with other tagged array components, superresolution imaging of live specimens will offer new understanding of cortical architecture and function.
Figures
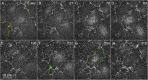
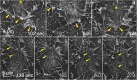
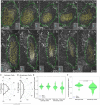
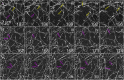
Similar articles
-
Architecture of the cortical actomyosin network driving apical constriction in C. elegans.J Cell Biol. 2023 Sep 4;222(9):e202302102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202302102. Epub 2023 Jun 23. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37351566 Free PMC article.
-
The RhoGEF protein Plekhg5 regulates medioapical and junctional actomyosin dynamics of apical constriction during Xenopus gastrulation.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Jun 1;34(7):ar64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-09-0411. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37043306 Free PMC article.
-
Micron-scale supramolecular myosin arrays help mediate cytoskeletal assembly at mature adherens junctions.J Cell Biol. 2022 Jan 3;221(1):e202103074. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202103074. Epub 2021 Nov 23. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34812842 Free PMC article.
-
RhoGTPases, actomyosin signaling and regulation of the epithelial Apical Junctional Complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Dec;36:194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25223584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Principles of Actomyosin Regulation In Vivo.Trends Cell Biol. 2019 Feb;29(2):150-163. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Trends Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30385150 Review.
Cited by
-
A new view of axon growth and guidance grounded in the stochastic dynamics of actin networks.Open Biol. 2023 Jun;13(6):220359. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220359. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37282493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchard GB, Murugesu S, Adams RJ, Martinez-Arias A, Gorfinkiel N (2010). Cytoskeletal dynamics and supracellular organisation of cell shape fluctuations during dorsal closure. Development 137, 2743–2752. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993). Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118, 401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

