Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulators (Riociguat) in Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from Real-Life Clinical Practice in a 3-Year Follow-Up
- PMID: 35544852
- PMCID: PMC9345144
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20210492
Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulators (Riociguat) in Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from Real-Life Clinical Practice in a 3-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a rare and complex disease with poor prognosis, which requires lifelong treatment.
Objective: To describe 3-year follow-up real-life data on treatment with soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators (Riociguat) of patients with PH, measuring current risk assessment parameters.
Methods: This study retrospectively collected clinical and epidemiological data of patients with PH of group 1 (pulmonary arterial hypertension) and group 4 (chronic thromboembolic PH). Non-invasive and invasive parameters corresponding to the risk assessment were analyzed at baseline and follow-up. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 18.0 software, and p-values < 0.050 were considered statistically significant.
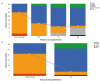
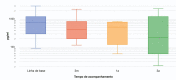
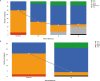
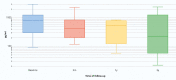
Results: In total, 41 patients receiving riociguat were included in the study. Of them, 31 had already completed 3 years of treatment and were selected for the following analysis. At baseline, 70.7% of patients were in WHO functional class III or IV. After 3 years of treatment, the WHO functional class significantly improved in all patients. In addition, the median of the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) significantly increased from 394 ± 91 m at baseline to 458 ± 100 m after 3 years of follow-up (p= 0.014). The three-year survival rate was 96.7%.
Conclusion: In our real-life cohort, most patients with PH treated with riociguat showed stable or improved risk parameters, especially in the 6MWT, at 3 years of follow-up.
Fundamento: A hipertensão pulmonar (HP) é uma doença rara e complexa com prognóstico ruim, que exige tratamento pela vida toda.
Objetivo: Descrever dados de 3 anos de acompanhamento da vida real sobre o tratamento com estimuladores de guanilato ciclase solúvel (Riociguate) de pacientes com HP, medindo parâmetros atuais de avaliação de risco.
Métodos: Coletamos dados clínicos e epidemiológicos retrospectivamente de pacientes com HP do grupo 1 (hipertensão arterial pulmonar) e do grupo 4 (HP tromboembólica crônica). Parâmetros não invasivos e invasivos correspondentes à avaliação de risco foram analisados na linha de base e no acompanhamento. Foram realizadas análises estatísticas usando o software SPSS 18.0, e os p-valores <0,050 foram considerados estatisticamente significativos.
Resultados: No total, 41 pacientes tratados com riociguate foram incluídos no estudo. Entre eles, 31 já concluíram 3 anos de tratamento e foram selecionados para a seguinte análise. Na linha de base, 70,7% dos pacientes estavam nas classes funcionais III ou IV da OMS. Depois de 3 anos de tratamento, a classe funcional da OMS melhorou significativamente em todos os pacientes. Além disso, a mediana do teste de caminhada de 6 minutos (TC6M) aumentou significativamente de 394 ± 91 m na linha de base para 458 ± 100 m após 3 anos de acompanhamento (p= 0,014). O índice de sobrevida após três anos foi de 96,7%.
Conclusão: Em nossa coorte de vida real, a maioria dos pacientes com HP tratados com riociguate demonstraram parâmetros de risco estáveis ou melhores, especialmente no TC6M, aos 3 anos de acompanhamento.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial conflito de interesse
Fernanda Brum Spilimbergo – Honorários de palestra e consultoria: Bayer, Eli Lilly e GSK.
Marcelo Bellon – Honorários de palestra e consultoria: Bayer, Eli Lilly e GSK.
Gabriela Roncato – Funcionária da Bayer
Gisela Martina Bohns Meyer – Honorários de palestra e consultoria: Bayer, Eli Lilly e GSK.
Figures




Comment in
-
Should we Consider the Stimulation of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase as Beneficial for Treating Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension?Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jun 10;118(6):1067-1068. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220261. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35703643 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
Riociguat: An Alternative to Treat Pulmonary Hypertension.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jul;119(1):111-112. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220305. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35830109 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Long-term clinical value and outcome of riociguat in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2019 Feb 28;22:163-168. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2019.02.004. eCollection 2019 Mar. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2019. PMID: 30859124 Free PMC article.
-
Riociguat for pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014 Nov 1;71(21):1839-44. doi: 10.2146/ajhp130777. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25320133 Review.
-
Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators in pulmonary hypertension.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;218:279-313. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-38664-0_12. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24092345 Review.
-
Safety and effectiveness of riociguat for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in real-world clinical practice: interim data from post-marketing surveillance in Japan.Pulm Circ. 2020 Jul 23;10(3):2045894020938986. doi: 10.1177/2045894020938986. eCollection 2020 Jul-Sep. Pulm Circ. 2020. PMID: 32754307 Free PMC article.
-
Riociguat: a novel new drug for treatment of pulmonary hypertension.Pharmacotherapy. 2015 May;35(5):502-19. doi: 10.1002/phar.1592. Pharmacotherapy. 2015. PMID: 26011143 Review.
Cited by
-
Should we Consider the Stimulation of Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase as Beneficial for Treating Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension?Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jun 10;118(6):1067-1068. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220261. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35703643 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
Meta-Analysis of Real-World Clinical Practice to Assess the Effectiveness of Riociguat in Treating Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2025 Feb;27(2):e70015. doi: 10.1111/jch.70015. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2025. PMID: 39957705 Free PMC article.
-
Riociguat: An Alternative to Treat Pulmonary Hypertension.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jul;119(1):111-112. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220305. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35830109 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
Prognostic Value of Serial Risk Stratification in Adult and Pediatric Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Systematic Review.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Jul 2;13(13):e034151. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.034151. Epub 2024 Jun 21. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38904230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM, et al. Survival in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension. Results from a National Prospective Registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115(5):343-9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-5-343. - PubMed
-
- Poch D, Mandel J. Pulmonary Hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(4):49-64. doi: 10.7326/AITC202104200. - PubMed
-
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Barst RJ, Badesch DB, Frost AE, McGoon MD. An Evaluation of Long-term Survival from Time of Diagnosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension from the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2012;142(2):448-56. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-1460. - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(1):67-119. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

