Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Evaluated by Office and Home Blood Pressure Measurements. TeleHBPM Study
- PMID: 35544853
- PMCID: PMC9345159
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20210504
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Evaluated by Office and Home Blood Pressure Measurements. TeleHBPM Study
Abstract
Background: Adequate treatment of arterial hypertension and achieving arterial hypertension goals in are important in reducing cardiovascular outcomes.
Objectives: To describe angiotensin receptor blockers in monotherapy or double combination therapy and the rate of arterial hypertension control.
Methods: This cross-sectional study evaluated patients who were using angiotensin receptor blockers between 2017 and 2020. Those using three or more antihypertensive drugs were excluded. The analyzed variables included sex, age, body mass index, valid home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) measurements, casual and HBPM systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements, blood pressure variability, and antihypertensive and angiotensin receptor blocker class. Paired t, chi-square, and Fisher's exact tests were used, as well as overlapping 95% confidence intervals and a significance level of 5% (p < 0.05).
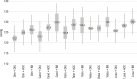
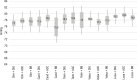
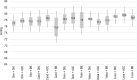
Results: Of 17,013 patients, 12,813 met the inclusion criteria, 62.1% of whom were female. The mean number of valid measurements was 23.3 (SD, 2.0). The mean HBPM and casual measurements for systolic blood pressure were 126.8 (SD, 15.8) mmHg and 133.5 (SD, 20.1) mmHg (p <0.001), respectively, while those for diastolic blood pressure were 79.1 (SD, 9.7 mmHg) and 83.6 (SD, 11.9) mmHg (p <0.001), respectively. Losartan was the most common angiotensin receptor blocker and resulted in the highest blood pressure values. Combinations of angiotensin receptor blockers with diuretics or calcium channel antagonists resulted in lower blood pressure values.
Conclusions: More than half of the patients used losartan, although it was the least efficient drug for reducing and controlling blood pressure.
Fundamento: O tratamento adequado e a obtenção das metas na hipertensão arterial são importantes na redução dos desfechos cardiovasculares.
Objetivos: Descrever os bloqueadores do receptor de angiotensina (BRA) em monoterapia ou combinação dupla e a taxa de controle da hipertensão arterial.
Métodos: Estudo transversal que avaliou pacientes em uso de BRA entre 2017 e 2020. Foram excluídos aqueles em uso de três ou mais anti-hipertensivos. As variáveis analisadas foram: sexo, idade, índice de massa corporal, medidas válidas da medida residencial da pressão arterial (MRPA); pressão arterial sistólica (PAS) e diastólica (PAD) obtidas pela MRPA e de forma casual; variabilidade pressórica; classe dos anti-hipertensivos e dos BRAs. Foram utilizados testes de t pareado, qui-quadrado e Fisher, além de sobreposição dos intervalos de confiança de 95% com nível de significância de 5% (p < 0,05).
Resultados: Foram selecionados 17.013 pacientes; destes, 12.813 preencheram os critérios, dos quais 62,1% eram do sexo feminino. O número médio de medidas válidas foi de 23,3 (±2,0), com médias para a PAS de 126,8±15,8 mmHg e 133,5±20,1 mmHg (p < 0,001) e para a PAD de 79,1±9,7 mmHg e 83,6±11,9 mmHg (p < 0,001) pela MRPA e medida casual, respectivamente. Losartana foi o BRA mais utilizado e o que apresentou comportamentos mais elevados da pressão arterial. As combinações de BRA com diuréticos ou com antagonistas de canal de cálcio tiveram menores valores de pressão arterial.
Conclusões: Losartana foi utilizada em mais da metade dos pacientes, apesar de ser a menos eficiente na redução e no controle da pressão arterial.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial conflito de interesse
Não há conflito com o presente artigo
Figures







Comment in
-
Differences among Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (BRA) in the Treatment of Arterial Hypertension.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jun 10;118(6):1083-1084. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220281. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35703644 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Task Force of the Latin American Society of Hypertension. Guidelines on the management of arterial hypertension and related comorbidities in Latin America. J Hypertens. 2017; 35: 1529-45. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018; 39: 3021-104. - PubMed
-
- Departamento da Sociedade Brasileira de Cardiologia. I Posicionamento Brasileiro sobre Fármacos Anti-hipertensivos. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2014; 102: 203-10.
-
- The Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Pharmacological blood pressure lowering for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease across different levels of blood pressure: an individual participant level data meta-analysis. LANCET. 2021; 397: 1625 - 1636. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

