COVID-19 and retinal degenerative diseases: Promising link "Kaempferol"
- PMID: 35544976
- PMCID: PMC9080119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102231
COVID-19 and retinal degenerative diseases: Promising link "Kaempferol"
Abstract
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak has caused unprecedented global disruption since 2020. Approximately 238 million people are affected worldwide where the elderly succumb to mortality. Post-COVID syndrome and its side effects have popped up with several health hazards, such as macular degeneration and vision loss. It thus necessitates better medical care and management of our dietary practices. Natural flavonoids have been included in traditional medicine and have also been used safely against COVID-19 and several other diseases. Kaempferol is an essential flavonoid that has been demonstrated to influence several vital cellular signaling pathways involved in apoptosis, angiogenesis, inflammation, and autophagy. In this review, we emphasize the plausible regulatory effects of Kaempferol on hallmarks of COVID-19 and macular degeneration.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement Nothing declared.
Figures
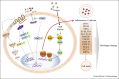
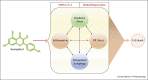
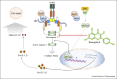
 represents the inhibition); Kaempferol- (PubChem CID5280863).
represents the inhibition); Kaempferol- (PubChem CID5280863).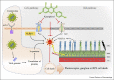
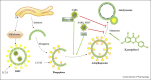
 represents the inhibition.
represents the inhibition.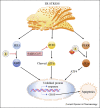
 represents the inhibition.
represents the inhibition.References
-
- Sim S.S., et al. Digital technology for AMD management in the post-COVID-19 new normal. Asia-Pac J Ophthalmol. 2021;10:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Abuse S., M.H.S. Administration . 2020. Double jeopardy: COVID-19 and behavioral health disparities for Black and Latino communities in the US.
-
- Yang J.M., et al. COVID-19 morbidity and severity in patients with age-related macular degeneration: a Korean nationwide cohort study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021:11881. - PMC - PubMed
-
Exudative AMD was found to be associated with an increased likelihood of susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The first study revealed the link between the risk of COVID-19 and its Ophthalmologic comorbidities and severe COVID-19 outcomes.
-
- Strauss O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:845–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

