Isotretinoin and its Metabolites Alter mRNA of Multiple Enzyme and Transporter Genes In Vitro, but Downregulation of Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide Does Not Translate to the Clinic
- PMID: 35545255
- PMCID: PMC11022860
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.122.000882
Isotretinoin and its Metabolites Alter mRNA of Multiple Enzyme and Transporter Genes In Vitro, but Downregulation of Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide Does Not Translate to the Clinic
Abstract
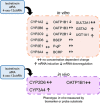
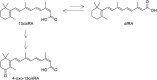
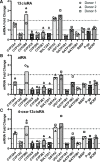
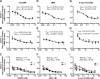
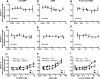
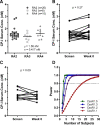
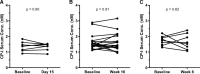
Isotretinoin [13-cis-retinoic acid (13cisRA)] is widely used for the treatment of neuroblastoma and acne. It acts via regulating gene transcription through binding to retinoic acid receptors. Yet, the potential for isotretinoin to cause transcriptionally mediated drug-drug interactions (DDIs) has not been fully explored. We hypothesized that isotretinoin and its active metabolites all-trans-retinoic acid (atRA) and 4-oxo-13cisRA would alter the transcription of enzymes and transporters in the human liver via binding to nuclear receptors. The goal of this study was to define the DDI potential of isotretinoin and its metabolites resulting from transcriptional regulation of cytochrome P450 and transporter mRNAs. In human hepatocytes (n = 3), 13cisRA, atRA, and 4-oxo-13cisRA decreased OATP1B1, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2D6 mRNA and increased CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 mRNA in a concentration-dependent manner. The EC50 values for OATP1B1 mRNA downregulation ranged from 2 to 110 nM, with maximum effect (Emax ) ranging from 0.17- to 0.54-fold. Based on the EC50 and Emax values and the known circulating concentrations of 13cisRA and its metabolites after isotretinoin dosing, a 55% decrease in OATP1B1 activity was predicted in vivo. In vivo DDI potential was evaluated clinically in participants dosed with isotretinoin for up to 32 weeks using coproporphyrin-I (CP-I) as an OATP1B1 biomarker. CP-I steady-state serum concentrations were unaltered following 2, 8, or 16 weeks of isotretinoin treatment. These data show that isotretinoin and its metabolites alter transcription of multiple enzymes and transporters in vitro, but translation of these changes to in vivo drug-drug interactions requires clinical evaluation for each enzyme. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Isotretinoin and its metabolites alter the mRNA expression of multiple cytochrome P450s (CYPs) and transporters in human hepatocytes, suggesting that isotretinoin may cause clinically significant drug-drug interactions (DDIs). Despite the observed changes in organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) mRNA in human hepatocytes, no clinical DDI was observed when measuring a biomarker, coproporphyrin-I. Further work is needed to determine whether these findings can be extrapolated to a lack of a DDI with CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 substrates.
Copyright © 2022 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Adedoyin A, Stiff DD, Smith DC, Romkes M, Bahnson RC, Day R, Hofacker J, Branch RA, Trump DL (1998) All-trans-retinoic acid modulation of drug-metabolizing enzyme activities: investigation with selective metabolic drug probes. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Barnett S, Ogungbenro K, Ménochet K, Shen H, Humphreys WG, Galetin A (2019) Comprehensive Evaluation of the Utility of 20 Endogenous Molecules as Biomarkers of OATP1B Inhibition Compared with Rosuvastatin and Coproporphyrin I. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 368:125–135. - PubMed
-
- Barnett S, Ogungbenro K, Ménochet K, Shen H, Lai Y, Humphreys WG, Galetin A (2018) Gaining Mechanistic Insight Into Coproporphyrin I as Endogenous Biomarker for OATP1B-Mediated Drug-Drug Interactions Using Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 104:564–574. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

