Applying evidence to practice by increasing intensity of intervention for children with severe speech sound disorder: a quality improvement project
- PMID: 35545259
- PMCID: PMC9096566
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjoq-2021-001761
Applying evidence to practice by increasing intensity of intervention for children with severe speech sound disorder: a quality improvement project
Abstract
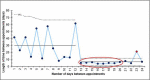
Speech sound disorder (SSD) affects up to 25% of UK children and may impact on: effective communication; the development of relationships; school progression and overall well-being. The evidence base shows that intervention for children with SSD is more effective and efficient when provided intensively in relation to the number of target sounds elicited in sessions (dose) and number of sessions per week (frequency). Southern Health and Social Care (HSC) Trust's baseline intensity of speech and language therapy (SLT) intervention was similar to that often found in current practice across the UK,where ~30 target sounds were elicited (dose) in once weekly sessions (frequency) over a 6-week block, followed by a break from therapy. This quality improvement (QI) project aimed to increase intensity of intervention for children with severe SSD within Southern HSC Trust's community SLT service to improve outcomes for children and their parents. QI methods supported accurate identification of ten 4-5 year olds with severe SSD and increased the intensity of their intervention over a 12-week period by measuring a range of data and speech outcomes. Findings showed a sustainable increase of dose (number of targets elicited per session) to levels recommended in the research (≥70). However, it was difficult to sustain increased frequency of appointments (to twice weekly) because of contextual factors such as sickness, etc. Accommodating this, measuring days between appointments captured an overall increase in the number of appointments attended across time. Child speech outcomes improved for direct speech measures and parent ratings of intelligibility. The intensive model of intervention has been implemented for children identified with severe SSD across Southern HSC Trust's community service with ongoing audit and development, and findings have been disseminated.
Keywords: PDSA; PRIMARY CARE; Paediatrics; Quality improvement.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- McLeod S, Baker E. Children’s Speech: An evidence-based approach to assessment and intervention. Sydney: Pearson, 2017.
-
- McLeod S, Harrison LJ, Wang C. A longitudinal population study of literacy and numeracy outcomes for children identified with speech, language, and communication needs in early childhood. Early Child Res Q 2019;47:507–17. 10.1016/j.ecresq.2018.07.004 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
