Activation of Xist by an evolutionarily conserved function of KDM5C demethylase
- PMID: 35545632
- PMCID: PMC9095838
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30352-1
Activation of Xist by an evolutionarily conserved function of KDM5C demethylase
Abstract
XX female and XY male therian mammals equalize X-linked gene expression through the mitotically-stable transcriptional inactivation of one of the two X chromosomes in female somatic cells. Here, we describe an essential function of the X-linked homolog of an ancestral X-Y gene pair, Kdm5c-Kdm5d, in the expression of Xist lncRNA, which is required for stable X-inactivation. Ablation of Kdm5c function in females results in a significant reduction in Xist RNA expression. Kdm5c encodes a demethylase that enhances Xist expression by converting histone H3K4me2/3 modifications into H3K4me1. Ectopic expression of mouse and human KDM5C, but not the Y-linked homolog KDM5D, induces Xist in male mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Similarly, marsupial (opossum) Kdm5c but not Kdm5d also upregulates Xist in male mESCs, despite marsupials lacking Xist, suggesting that the KDM5C function that activates Xist in eutherians is strongly conserved and predates the divergence of eutherian and metatherian mammals. In support, prototherian (platypus) Kdm5c also induces Xist in male mESCs. Together, our data suggest that eutherian mammals co-opted the ancestral demethylase KDM5C during sex chromosome evolution to upregulate Xist for the female-specific induction of X-inactivation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
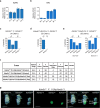
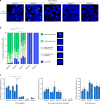
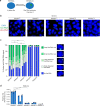
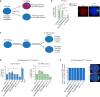
Similar articles
-
Divergent DNA methylation dynamics in marsupial and eutherian embryos.Nature. 2025 Jun;642(8069):1073-1079. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08992-2. Epub 2025 May 14. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40369084 Free PMC article.
-
KDM6A facilitates Xist upregulation at the onset of X inactivation.Biol Sex Differ. 2025 Jan 3;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00683-3. Biol Sex Differ. 2025. PMID: 39754175 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution from XIST-independent to XIST-controlled X-chromosome inactivation: epigenetic modifications in distantly related mammals.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 25;6(4):e19040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019040. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21541345 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted role of CTCF in X-chromosome inactivation.Chromosoma. 2024 Oct;133(4):217-231. doi: 10.1007/s00412-024-00826-w. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Chromosoma. 2024. PMID: 39433641 Review.
-
X chromosome inactivation in mammals: general principles and species-specific considerations.EMBO Rep. 2025 Jul;26(14):3478-3490. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00499-1. Epub 2025 Jun 19. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 40537514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal sex specific brain gene expression pattern during early rat embryonic development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 19;12:1343800. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1343800. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38961864 Free PMC article.
-
The histone demethylase KDM5C controls female bone mass by promoting energy metabolism in osteoclasts.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 23:2023.02.23.529728. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529728. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Adv. 2023 Apr 5;9(14):eadg0731. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg0731. PMID: 36865269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The histone demethylase KDM5C controls female bone mass by promoting energy metabolism in osteoclasts.Sci Adv. 2023 Apr 5;9(14):eadg0731. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg0731. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37018401 Free PMC article.
-
KDM5C and KDM5D mutations have different consequences in clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells.Commun Biol. 2025 Feb 15;8(1):244. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07695-8. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39955388 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually Dimorphic Alterations in the Transcriptome and Behavior with Loss of Histone Demethylase KDM5C.Cells. 2023 Feb 16;12(4):637. doi: 10.3390/cells12040637. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohno, S. In Sex Chromosomes and Sex-linked Genes, x, 192 (Springer-Verlag, 1967).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

