Minimal handgrip force is needed for transcutaneous electrical stimulation to improve hand functions of patients with severe spinal cord injury
- PMID: 35545644
- PMCID: PMC9095635
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11306-5
Minimal handgrip force is needed for transcutaneous electrical stimulation to improve hand functions of patients with severe spinal cord injury
Abstract
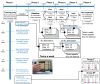
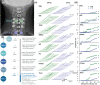
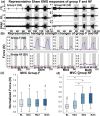
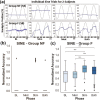
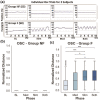
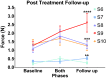
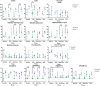
Spinal cord stimulation enhanced restoration of motor function following spinal cord injury (SCI) in unblinded studies. To determine whether training combined with transcutaneous electrical spinal cord stimulation (tSCS), with or without systemic serotonergic treatment with buspirone (busp), could improve hand function in individuals with severe hand paralysis following SCI, we assessed ten subjects in a double-blind, sham-controlled, crossover study. All treatments-busp, tSCS, and the busp plus tSCS-reduced muscle tone and spasm frequency. Buspirone did not have any discernible impact on grip force or manual dexterity when administered alone or in combination with tSCS. In contrast, grip force, sinusoidal force generation and grip-release rate improved significantly after 6 weeks of tSCS in 5 out of 10 subjects who had residual grip force within the range of 0.1-1.5 N at the baseline evaluation. Improved hand function was sustained in subjects with residual grip force 2-5 months after the tSCS and buspirone treatment. We conclude that tSCS combined with training improves hand strength and manual dexterity in subjects with SCI who have residual grip strength greater than 0.1 N. Buspirone did not significantly improve the hand function nor add to the effect of stimulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.C.L has shareholder interest in Onward and Restore Technologies. V.R.E. has shareholder interest in Onward and SpineX. PG has shareholder interest in SpineX. After ending affiliation with UCLA, L.M. gained employment at Boston Scientific Corporation and later became a stakeholder in Boston Scientific Corporation. The content of this publication is under the sole responsibility of its author/publisher and does not represent the views or opinions of Boston Scientific Corporation. All the other authors have no competing-interest (R.H., A.A.N., S.Z., E.M., T.S., D.S., T.L., T.H., M.M., M.A., M.A., Y.Z., M.R.N., M.S., and J.C.L.).
Figures
References
-
- Freehafer AA. Care of the hand in cervical spinal cord injuries. Paraplegia. 1969;7:118–130. - PubMed

