Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside inhibits the β-catenin/MGMT pathway by upregulating miR-214-5p to reverse chemotherapy resistance in glioma cells
- PMID: 35545654
- PMCID: PMC9095653
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11757-w
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside inhibits the β-catenin/MGMT pathway by upregulating miR-214-5p to reverse chemotherapy resistance in glioma cells
Abstract
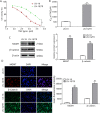
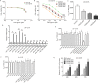
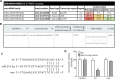
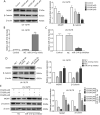
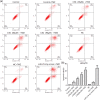
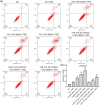
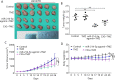
Overcoming resistance to alkylating agents has important clinical significance in glioma. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G) has a tumor-suppressive effect on tumor cells. However, whether it plays a role in temozolomide resistance in glioma is still unclear. We constructed a TMZ-resistant LN-18/TR glioma cell line, observed the effect of C3G on TMZ resistance in this cell line, and explored the role of miR-214-5p in chemoresistance. Results showed that β-catenin and MGMT were significantly upregulated in LN-18/TR cells. C3G upregulated miR-214-5p and enhanced the cytotoxic effect of temozolomide on LN-18/TR cells. Contrarily, C3G downregulated β-catenin and MGMT. Moreover, the miR-214-5p mimic downregulated β-catenin and MGMT in LN-18/TR cells, whereas the miR-214-5p inhibitor had the opposite effect; the miR-214-5p inhibitor significantly blocked the C3G-induced downregulation of β-catenin and MGMT. C3G or the miR-214-5p mimic enhanced temozolomide-induced apoptosis in LN-18/TR cells, whereas the miR-214-5p inhibitor blocked this effect. Furthermore, C3G or miR-214-5p agomir combined with TMZ significantly inhibited the growth of LN-18/TR tumors. Collectively, our research discovered the potential signaling mechanism associated with C3G-mediated suppression of TMZ resistance in LN-18/TR cells through miR-214-5p, which can facilitate the treatment of MGMT-induced resistance in glioma cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overcoming temozolomide resistance in glioma: recent advances and mechanistic insights.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Jun 5;13(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02046-4. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40468460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of temozolomide resistance in glioma cells via the RIP2/NF-κB/MGMT pathway.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 May;27(5):552-563. doi: 10.1111/cns.13591. Epub 2021 Jan 18. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021. PMID: 33460245 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of LncRNA HOTAIR is a risk factor for temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via activation of the miR-214/β-catenin/MGMT pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 31;14(1):26224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77348-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39482401 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA UCA1/miR-182-5p/MGMT axis modulates glioma cell sensitivity to temozolomide through MGMT-related DNA damage pathways.Hum Pathol. 2022 May;123:59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2022.02.016. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Hum Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35219686
-
A novel approach to overcome temozolomide resistance in glioma and melanoma: Inactivation of MGMT by gene therapy.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Mar 18;406(3):311-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.042. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21329652 Review.
Cited by
-
Biology and Development of DNA-Targeted Drugs, Focusing on Synthetic Lethality, DNA Repair, and Epigenetic Modifications for Cancer: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 6;25(2):752. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020752. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platycodin D Enhances Glioma Sensitivity to Temozolomide by Inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Mar 11;19:1811-1824. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S503167. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40093646 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the impact of circRNA-mediated autophagy on tumor therapeutic resistance: a novel perspective.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Apr 26;29(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00571-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38671354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling Pathways and Natural Compounds in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line.Molecules. 2022 Jun 7;27(12):3661. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123661. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744786 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming temozolomide resistance in glioma: recent advances and mechanistic insights.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Jun 5;13(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02046-4. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40468460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

