Young CSF restores oligodendrogenesis and memory in aged mice via Fgf17
- PMID: 35545674
- PMCID: PMC9377328
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04722-0
Young CSF restores oligodendrogenesis and memory in aged mice via Fgf17
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Young CSF restores oligodendrogenesis and memory in aged mice via Fgf17.Nature. 2023 Jan;613(7942):E1. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05630-z. Nature. 2023. PMID: 36513761 No abstract available.
Abstract
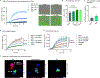
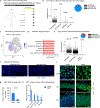
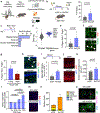
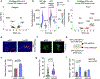
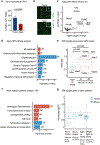
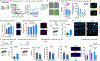
Recent understanding of how the systemic environment shapes the brain throughout life has led to numerous intervention strategies to slow brain ageing1-3. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) makes up the immediate environment of brain cells, providing them with nourishing compounds4,5. We discovered that infusing young CSF directly into aged brains improves memory function. Unbiased transcriptome analysis of the hippocampus identified oligodendrocytes to be most responsive to this rejuvenated CSF environment. We further showed that young CSF boosts oligodendrocyte progenitor cell (OPC) proliferation and differentiation in the aged hippocampus and in primary OPC cultures. Using SLAMseq to metabolically label nascent mRNA, we identified serum response factor (SRF), a transcription factor that drives actin cytoskeleton rearrangement, as a mediator of OPC proliferation following exposure to young CSF. With age, SRF expression decreases in hippocampal OPCs, and the pathway is induced by acute injection with young CSF. We screened for potential SRF activators in CSF and found that fibroblast growth factor 17 (Fgf17) infusion is sufficient to induce OPC proliferation and long-term memory consolidation in aged mice while Fgf17 blockade impairs cognition in young mice. These findings demonstrate the rejuvenating power of young CSF and identify Fgf17 as a key target to restore oligodendrocyte function in the ageing brain.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
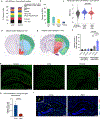
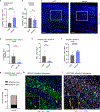
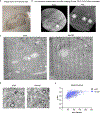


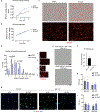



Comment in
-
Transcriptomic mapping of the human cerebrovasculature.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Jun;18(6):319-320. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00650-9. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35322261 No abstract available.
-
Young cerebrospinal fluid improves memory in old mice.Nature. 2022 May;605(7910):428-429. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-00860-7. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35546616 No abstract available.
-
Restoring the aged brain with CSF.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Jul;23(7):393. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00610-8. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35668296 No abstract available.
-
Restored oligodendrogenesis by fibroblast growth factor 17: molecular mechanism for rejuvenating ageing-related memory deficit.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 16;7(1):237. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01092-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35842438 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CSF factors in memory function.Lancet Neurol. 2022 Sep;21(9):765-767. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00296-4. Lancet Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35963250 No abstract available.
References
Main text references
Methods references
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

