Small molecules of herbal origin for osteoarthritis treatment: in vitro and in vivo evidence
- PMID: 35545776
- PMCID: PMC9092710
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02785-y
Small molecules of herbal origin for osteoarthritis treatment: in vitro and in vivo evidence
Abstract
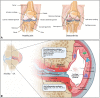
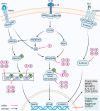
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common musculoskeletal degenerative diseases and contributes to heavy socioeconomic burden. Current pharmacological and conventional non-pharmacological therapies aim at relieving the symptoms like pain and disability rather than modifying the underlying disease. Surgical treatment and ultimately joint replacement arthroplasty are indicated in advanced stages of OA. Since the underlying mechanisms of OA onset and progression have not been fully elucidated yet, the development of novel therapeutics to prevent, halt, or reverse the disease is laborious. Recently, small molecules of herbal origin have been reported to show potent anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic, and anabolic effects, implying their potential for treatment of OA. Herein, the molecular mechanisms of these small molecules, their effect on physiological or pathological signaling pathways, the advancement of the extraction methods, and their potential clinical translation based on in vitro and in vivo evidence are comprehensively reviewed.
Keywords: Anabolic; Anti-catabolic; Anti-inflammatory; Compound delivery; Herbal extraction; Herbal medicine; Inflammation; Therapeutic target; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2163–2196. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Nolte S, Ackerman I, Fransen M, Bridgett L, Williams S, Guillemin F, Hill CL. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323–1330. - PubMed
-
- Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H, Carr AJ. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376–387. - PubMed
-
- Palazzo C, Nguyen C, Lefevre-Colau M-M, Rannou F, Poiraudeau S. Risk factors and burden of osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(3):134–138. - PubMed
-
- Jordan KP, Jöud A, Bergknut C, Croft P, Edwards JJ, Peat G, Petersson IF, Turkiewicz A, Wilkie R, Englund M. International comparisons of the consultation prevalence of musculoskeletal conditions using population-based healthcare data from England and Sweden. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(1):212–218. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

