Effect of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy on SDF-1 and CXCR4 in epithelial ovarian cancer and its prognosis
- PMID: 35545781
- PMCID: PMC9092776
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02621-2
Effect of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy on SDF-1 and CXCR4 in epithelial ovarian cancer and its prognosis
Abstract
Background: The effect of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy on the expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and receptor CXCR4 in epithelial ovarian cancer tumor cells and its prognosis are unknown. Our work aimed to investigate the effect of chemotherapy +/- bevacizumab on these markers and the impact of this treatment modality in clinical outcomes.
Methods: Altogether 68 patients with epithelial ovarian cancer who were treated with chemotherapy in our hospital from June 2018 to June 2019 were selected. It was an open-labeled and controlled clinical trial (ethical approval no. 20180435). The patients were grouped according to their admission order. Patients treated with paclitaxel and carboplatin were included in group A, while patients treated with bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin were included in group B. qRT-PCR was used to detect the changes of SDF-1 and CXCR4 before and after chemotherapy. Various clinical indicators of patients in the two groups were recorded to analyze the clinical efficacy, and safety of different treatment modalities and the prognosis of the two groups was analyzed.
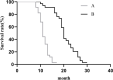
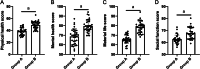
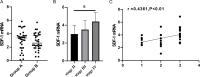
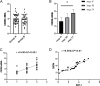
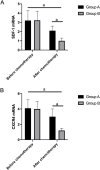
Results: The relative expression of SDF-1 and CXCR4 was positively correlated with epithelial ovarian cancer stages (P<0.00). Together, SDF-1 and CXCR4 were positively correlated in epithelial ovarian cancer staging (P<0.001). SDF-1 and CXCR4 in both groups after chemotherapy were significantly decreased (P<0.001), and the downregulation of SDF-1 and CXCR4 expression in group B was significantly higher than that in group A after chemotherapy (P<0.001). No significant difference in the metastasis rates of the two groups before chemotherapy was observed (P>0.05), but the recurrence rate after 1 year was lower in group B than in group A (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Adding bevacizumab diminished the expression of related cancer markers SDF-1 and CXCR4 more than chemotherapy alone in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Furthermore, better rates of recurrence with no concerns regarding adverse drug reactions or quality of life were seen in bevacizumab plus chemotherapy group.
Keywords: Bevacizumab; CXCR4; Chemotherapy; Epithelial ovarian cancer; SDF-1.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

