Towards Upcycling Biomass-Derived Crosslinked Polymers with Light
- PMID: 35545813
- PMCID: PMC9400847
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202203353
Towards Upcycling Biomass-Derived Crosslinked Polymers with Light
Abstract
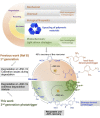
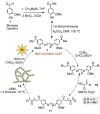
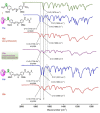
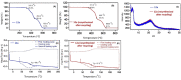
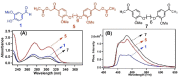
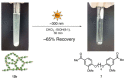
Photodegradable, recyclable, and renewable, crosslinked polymers from bioresources show promise towards developing a sustainable strategy to address the issue of plastics degradability and recyclability. Photo processes are not widely exploited for upcycling polymers in spite of the potential to have spatial and temporal control of the degradation in addition to being a green process. In this report we highlight a methodology in which biomass-derived crosslinked polymers can be programmed to degrade at ≈300 nm with ≈60 % recovery of the monomer. The recovered monomer was recycled back to the crosslinked polymer.
Keywords: Biomass; Photodegradation; Phototriggered Materials; Polymer Degradation; Upcycling.
© 2022 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Besson M., Gallezot P., Pinel C., Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1827–1870. - PubMed
-
- Binder J. B., Raines R. T., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1979–1985. - PubMed
-
- Alonso D. M., Wettstein S. G., Dumesic J. A., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 8075–8098. - PubMed
-
- Brutman J. P., De Hoe G. X., Schneiderman D. K., Le T. N., Hillmyer M. A., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11097–11106.
-
- Corma A., Iborra S., Velty A., Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2411–2502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

