Neural sampling machine with stochastic synapse allows brain-like learning and inference
- PMID: 35546144
- PMCID: PMC9095718
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30305-8
Neural sampling machine with stochastic synapse allows brain-like learning and inference
Abstract
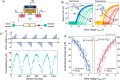
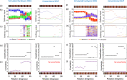
Many real-world mission-critical applications require continual online learning from noisy data and real-time decision making with a defined confidence level. Brain-inspired probabilistic models of neural network can explicitly handle the uncertainty in data and allow adaptive learning on the fly. However, their implementation in a compact, low-power hardware remains a challenge. In this work, we introduce a novel hardware fabric that can implement a new class of stochastic neural network called Neural Sampling Machine (NSM) by exploiting the stochasticity in the synaptic connections for approximate Bayesian inference. We experimentally demonstrate an in silico hybrid stochastic synapse by pairing a ferroelectric field-effect transistor (FeFET)-based analog weight cell with a two-terminal stochastic selector element. We show that the stochastic switching characteristic of the selector between the insulator and the metallic states resembles the multiplicative synaptic noise of the NSM. We perform network-level simulations to highlight the salient features offered by the stochastic NSM such as performing autonomous weight normalization for continual online learning and Bayesian inferencing. We show that the stochastic NSM can not only perform highly accurate image classification with 98.25% accuracy on standard MNIST dataset, but also estimate the uncertainty in prediction (measured in terms of the entropy of prediction) when the digits of the MNIST dataset are rotated. Building such a probabilistic hardware platform that can support neuroscience inspired models can enhance the learning and inference capability of the current artificial intelligence (AI).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Yu, S. et al. Scaling-up resistive synaptic arrays for neuro-inspired architecture: challenges and prospect. In Technical Digest—International Electron Devices Meeting, IEDM (2015).
-
- Gao, L. et al. Fully parallel write/read in resistive synaptic array for accelerating on-chip learning. Nanotechnology26, 455204 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Ambrogio, S. et al. Equivalent-accuracy accelerated neural-network training using analogue memory. Nature558, 60–67 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Kuzum, D., Jeyasingh, R. G. D., Lee, B. & Wong, H. S. P. Nanoelectronic programmable synapses based on phase change materials for brain-inspired computing. Nano Lett. 12, 2179–2186 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Burr, G. W. et al. Experimental demonstration and tolerancing of a large-scale neural network (165 000 synapses) using phase-change memory as the synaptic weight element. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices62, 3498–3507 (2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

