Presurgical selection of the ideal aneurysm clip by the use of a three-dimensional planning system
- PMID: 35546216
- PMCID: PMC9349090
- DOI: 10.1007/s10143-022-01794-4
Presurgical selection of the ideal aneurysm clip by the use of a three-dimensional planning system
Abstract
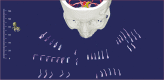
Aneurysm occlusion rate after clipping is higher than after endovascular treatment. However, a certain percentage of incompletely clipped aneurysms remains. Presurgical selection of the proper aneurysm clips could potentially reduce the rate of incomplete clippings caused by inadequate clip geometry. The aim of the present study was to assess whether preoperative 3D image-based simulation allows for preoperative selection of a proper aneurysm clip for complete occlusion in individual cases. Patients harboring ruptured or unruptured cerebral aneurysms prior to surgical clipping were analyzed. CT angiography images were transferred to a 3D surgical-planning station (Dextroscope®) with imported models of 58 aneurysm clips. Intracranial vessels and aneurysms were segmented and the virtual aneurysm clips were placed at the aneurysm neck. Operating surgeons had information about the selected aneurysm clip, and patients underwent clipping. Intraoperative clip selection was documented and aneurysm occlusion rate was assessed by postoperative digital subtraction angiography. Nineteen patients were available for final analysis. In all patients, the most proximal clip at the aneurysm neck was the preselected clip. All aneurysms except one were fully occluded, as assessed by catheter angiography. One aneurysm had a small neck remnant that did not require secondary surgery and was occluded 15 months after surgery. 3D image-based preselection of a proper aneurysm clip can be translated to the operating room and avoids intraoperative clip selection. The associated occlusion rate of aneurysms is high.
Keywords: Aneurysm remnant; Cerebral aneurysm; Clipping; Simulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ES and RK declare no competing interests; AK is a consultant to Brainlab; MG is a consultant to Medtronic, Abbott, LivaNova, and Nevro; FR receives royalties from Spineart, is a consultant to Spineart, Brainlab, Stryker, Interventional Systems, and receives money for presentations from Spineart, Stryker, and Icotec.
Figures


References
-
- Mori K, Wada K, Otani N, Tomiyama A, Toyooka T, Takeuchi S, Yamamoto T, Nakao Y, Arai H (2018) Keyhole strategy aiming at minimizing hospital stay for surgical clipping of unruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg:1–8. 10.3171/2017.10.JNS171973 - PubMed
-
- Sun H, Safavi-Abbasi S, Spetzler RF. Retractorless surgery for intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg Sci. 2016;60:54–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

