Brain region-specific effects of nearly fixed sapiens-derived alleles
- PMID: 35546225
- PMCID: PMC9097168
- DOI: 10.1186/s12863-022-01048-8
Brain region-specific effects of nearly fixed sapiens-derived alleles
Abstract
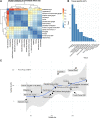
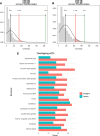
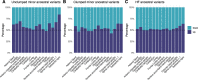
The availability of high-coverage genomes of our extinct relatives, the Neanderthals and Denisovans, and the emergence of large, tissue-specific databases of modern human genetic variation, offer the possibility of probing the effects of modern-derived alleles in specific tissues, such as the brain, and its specific regions. While previous research has explored the effects of introgressed variants in gene expression, the effects of Homo sapiens-specific gene expression variability are still understudied. Here we identify derived, Homo sapiens-specific high-frequency (≥90%) alleles that are associated with differential gene expression across 15 brain structures derived from the GTEx database. We show that regulation by these derived variants targets regions under positive selection more often than expected by chance, and that high-frequency derived alleles lie in functional categories related to transcriptional regulation. Our results highlight the role of these variants in gene regulation in specific regions like the cerebellum and pituitary.
Keywords: Brain; Gene regulation; Human evolution; cis-eQTL.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
